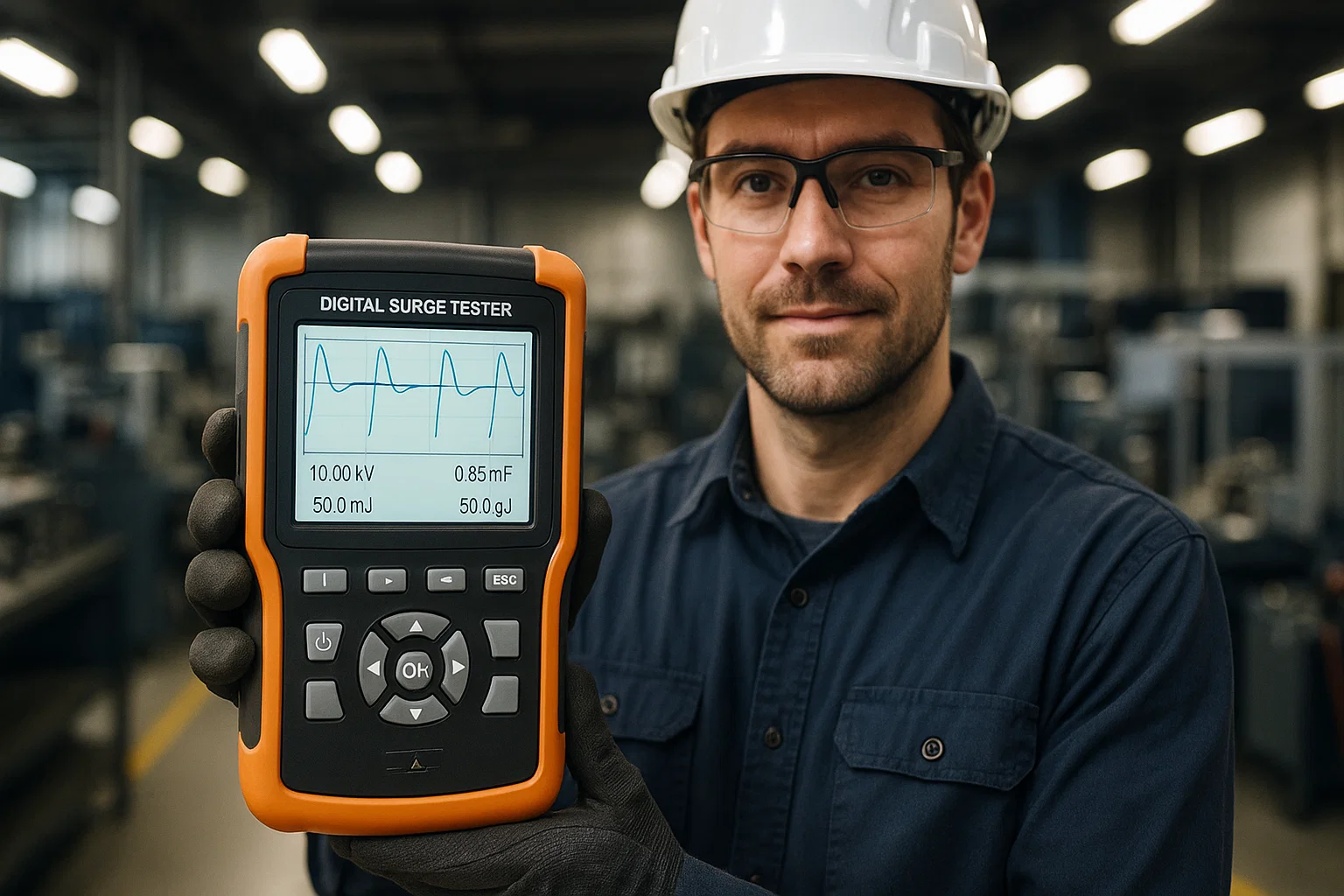
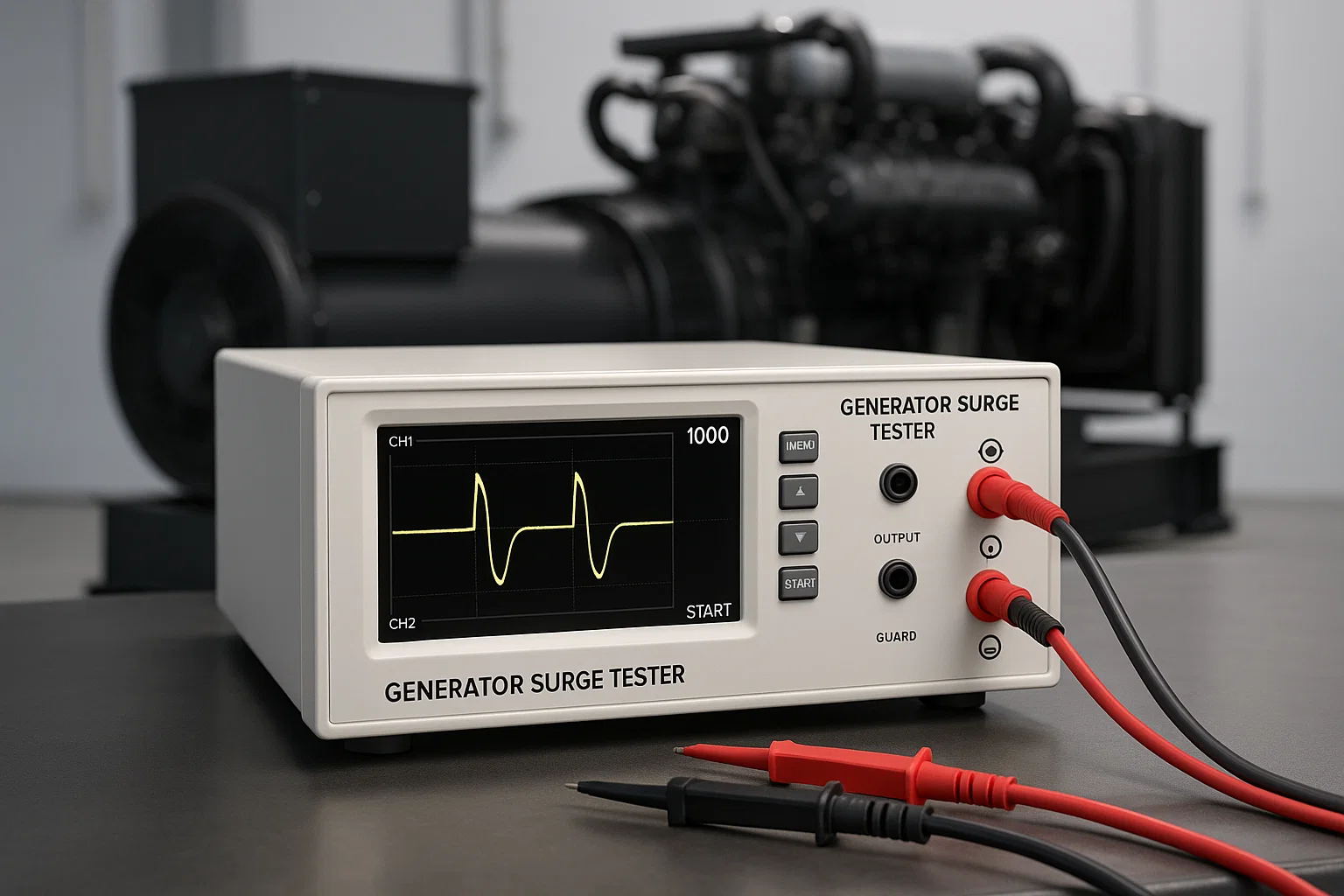

Struggling with unclear test readings and outdated analog gauges that compromise your electrical testing accuracy? Traditional testing equipment often leaves technicians guessing, leading to costly mistakes and equipment failures. An LCD based tester revolutionizes electrical diagnostics with crystal-clear digital displays, precise measurements, and intuitive interfaces that transform complex testing into straightforward, reliable processes.

An LCD based tester is a sophisticated electrical diagnostic instrument equipped with a liquid crystal display screen that provides real-time, accurate measurements and visual representations of electrical parameters. Unlike their analog predecessors with needle gauges and limited readability, LCD based testers offer digital precision, data logging capabilities, and enhanced user interfaces that streamline the testing process.
These advanced instruments have become indispensable in industrial maintenance, quality control, and electrical troubleshooting. The LCD screen serves as the command center, displaying voltage levels, waveform patterns, resistance measurements, and diagnostic alerts with remarkable clarity.
Liquid Crystal Display technology works by manipulating light through liquid crystal molecules sandwiched between two polarizing filters. When electrical current passes through these crystals, they align to either block or allow light passage, creating the visual information you see on screen.
Key technological advantages include:
The electrical testing landscape features several categories of LCD equipped diagnostic tools, each designed for specific testing requirements.
Digital surge testers represent one of the most sophisticated applications of LCD technology in electrical testing. These instruments detect insulation weaknesses, turn-to-turn faults, and winding irregularities in motors, transformers, and generators.
Display capabilities include:
LCD based multimeters have evolved from simple voltage meters into comprehensive diagnostic platforms. Modern versions display simultaneous measurements, auto-ranging functions, and graphical representations of electrical parameters.
These specialized testers combine surge testing, insulation resistance, and winding resistance measurements. The LCD interface provides comprehensive motor diagnostics through intuitive menu navigation and clear visual feedback.
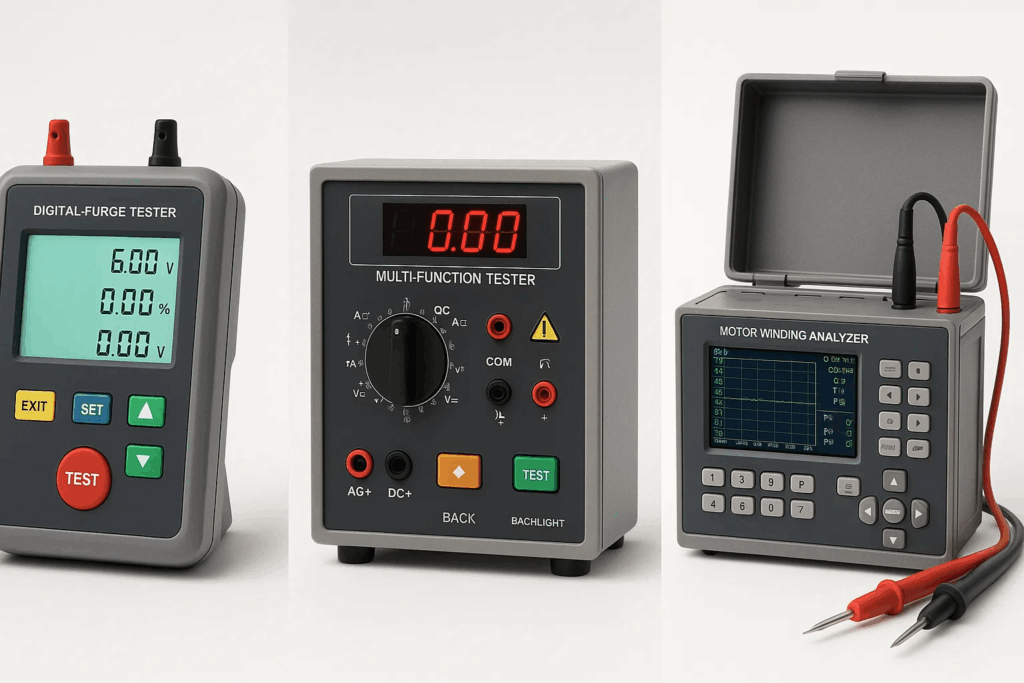

The display quality directly impacts testing efficiency and accuracy. Premium LCD based testers incorporate:
Screen resolution: High-definition displays (minimum 320×240 pixels) ensure crisp waveform rendering and text clarity.
Backlight technology: LED backlighting with adjustable brightness adapts to different working environments, from dimly lit substations to bright outdoor installations.
Touchscreen capabilities: Advanced models feature capacitive touchscreens for intuitive menu navigation and quick parameter adjustments.
Information density: Well-designed interfaces balance comprehensive data presentation with visual simplicity, preventing information overload.
Modern LCD based testers transcend basic measurement display by offering robust data management features:
The LCD display’s ability to show precise numerical values extends testing capabilities beyond analog limitations. Digital resolution allows:
Digital precision eliminates the parallax error and interpolation guesswork inherent in analog meters. When testing motor windings or analyzing surge test results, every decimal point matters. LCD displays present exact values, ensuring consistent, repeatable measurements across different operators and testing sessions.
Time efficiency translates directly to cost savings in industrial settings. LCD based testers accelerate diagnostics through:
Instant measurement display: No waiting for needle stabilization or manual calculation
Automated test sequences: Pre-programmed routines run multiple tests with minimal operator intervention
Quick result interpretation: Color-coded pass/fail indicators eliminate ambiguity
Batch testing capabilities: Store and compare multiple assets simultaneously
Quality management systems demand thorough documentation. LCD based testers excel in creating audit trails through:
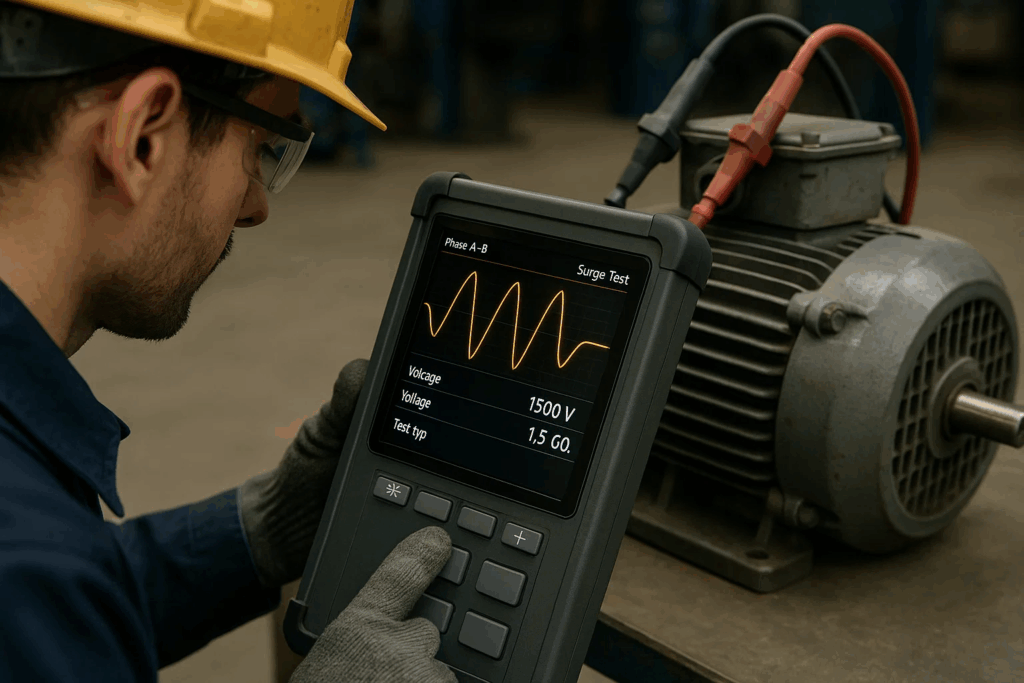
Production facilities rely on LCD based testers for incoming inspection, in-process verification, and final product validation. The visual feedback ensures every motor, transformer, or electrical component meets stringent quality standards before reaching customers.
Surge testing enhances motor reliability by identifying developing faults before catastrophic failures occur. LCD displays reveal subtle changes in waveform patterns that indicate deteriorating insulation or developing shorts, enabling scheduled maintenance rather than emergency repairs.
Utilities and independent power producers use LCD based testers for:
From electric vehicle motor testing to railway traction motor diagnostics, LCD based instruments provide the precision required in modern transportation systems.
Before investing in equipment, clearly define your testing scope:
What types of equipment will you test? Motors, generators, transformers, or general electrical systems?
What voltage levels are involved? Low-voltage control circuits or high-voltage power systems?
What testing standards must you meet? IEEE, IEC, or industry-specific requirements?
How frequently will you conduct tests? Daily production testing or periodic maintenance checks?
When choosing the right surge tester, evaluate these critical parameters:
Voltage output range: Ensure the tester covers your maximum test voltage requirements with adequate safety margin
Sensitivity levels: Higher sensitivity detects smaller defects but may increase false positives
Test modes available: Surge comparison, hipot, insulation resistance, and winding resistance in one platform
Display size and resolution: Larger screens facilitate team diagnostics and training
Environmental ratings: IP protection levels for harsh industrial environments
While LCD based testers represent significant initial investments, consider:

Successful testing begins before connecting any leads:
Equipment inspection: Verify the LCD display functions correctly, test leads show no damage, and battery charge is adequate
Safety verification: Confirm proper lockout/tagout procedures, voltage de-energization, and personal protective equipment
Environmental assessment: Ensure adequate lighting, stable work surface, and appropriate ambient conditions
Test plan review: Confirm testing sequence, acceptance criteria, and documentation requirements
Quality test results depend on proper technique:
Understanding what the screen tells you requires training and experience. When troubleshooting common surge tester errors, look for:
Waveform shape deviations: Spikes, dips, or irregular patterns indicating specific fault types
Numerical threshold violations: Values outside acceptable ranges per manufacturer specifications
Comparative analysis results: Differences between phases or coils exceeding tolerance limits
Trend indicators: Progressive degradation visible in historical data
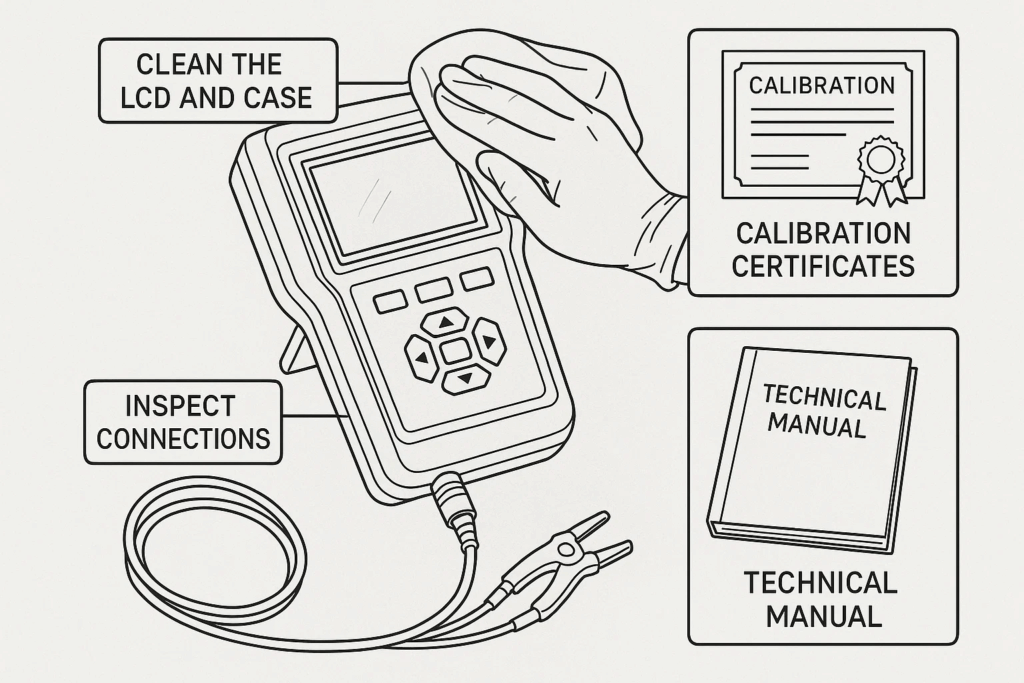
Protecting your investment requires consistent care:
Display cleaning: Use microfiber cloths and approved cleaners to prevent screen damage
Connection maintenance: Inspect and clean test lead connectors regularly
Battery management: Follow proper charging cycles to maximize battery life
Firmware updates: Install manufacturer updates to access new features and improvements
Storage conditions: Maintain appropriate temperature and humidity when not in use
Measurement accuracy depends on regular calibration. Learn how to maintain and calibrate your digital surge tester following these guidelines:
Dim or faded screen: Check backlight settings, battery voltage, or brightness adjustment options
Unresponsive touchscreen: Clean the screen surface, verify calibration, or restart the device
Pixel anomalies: Minor dead pixels rarely affect functionality, but widespread issues require professional service
Erratic readings: Verify connection quality, check for electromagnetic interference, or assess environmental factors
Out-of-range results: Confirm proper test mode selection, voltage settings, and equipment compatibility
Communication errors: Inspect cables, verify software versions, and check connection protocols
While LCD technology remains dominant, emerging innovations promise enhanced capabilities:
OLED displays offering deeper blacks, wider color gamut, and improved energy efficiency
E-paper technology providing sunlight-readable displays with minimal power consumption
Augmented reality overlays projecting diagnostic information onto equipment being tested
Flexible displays enabling new form factors and rugged designs
Modern LCD based testers increasingly connect to Industrial Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystems:
An LCD based tester delivers maximum value when:
Consider these factors when calculating ROI:
Prevented failures: Average cost of unplanned downtime multiplied by early detection rate
Labor savings: Reduced testing time converted to hourly labor costs
Quality improvements: Reduction in warranty claims or customer complaints
Extended asset life: Deferred replacement costs through better maintenance
Regulatory compliance: Avoided penalties and audit costs

LCD based testers provide precise digital measurements with no parallax error, comprehensive data logging, waveform visualization, and intuitive user interfaces that improve accuracy and efficiency.
Annual calibration by certified laboratories is standard, with interim verification checks recommended quarterly or after any suspected accuracy issues.
Yes, industrial-grade models feature ruggedized housings, sealed connectors, and wide operating temperature ranges suitable for demanding environments.
With proper maintenance and care, quality LCD based testers typically provide 10-15 years of reliable service, though technology upgrades may drive earlier replacement.
Modern devices feature intuitive interfaces with guided workflows that minimize training time. Most operators become proficient within days of structured training.
LCD based testers represent the convergence of digital precision, user-friendly design, and comprehensive diagnostic capabilities. From manufacturing quality control to predictive maintenance programs, these instruments deliver the accuracy, efficiency, and documentation modern electrical testing demands.
The transition from analog to digital testing equipment parallels the broader industrial digitalization trend. Organizations investing in LCD based testers gain not just superior measurement tools, but strategic assets that enhance reliability, reduce costs, and provide competitive advantages through superior equipment maintenance.
Whether you’re upgrading legacy testing equipment or establishing new testing capabilities, LCD based testers offer proven technology backed by continuous innovation. The clear displays, intuitive interfaces, and comprehensive data management transform complex electrical diagnostics into streamlined, reliable processes that anyone can master with proper training.
Take the next step toward testing excellence. Evaluate your current testing procedures, identify accuracy and efficiency gaps, and explore how LCD based testers can elevate your electrical maintenance program. The investment in precision today prevents the costly failures of tomorrow.
Ready to upgrade your electrical testing capabilities? Explore our comprehensive range of LCD based testing solutions designed for accuracy, reliability, and ease of use.