

Manufacturing facilities lose millions annually due to undetected motor failures and inefficient quality control processes. Traditional manual testing methods consume valuable production time while introducing human error that compromises reliability. Automated motor testing systems eliminate these bottlenecks, delivering quantifiable returns through enhanced accuracy, accelerated testing cycles, and predictive maintenance capabilities that prevent costly equipment failures before they disrupt operations.
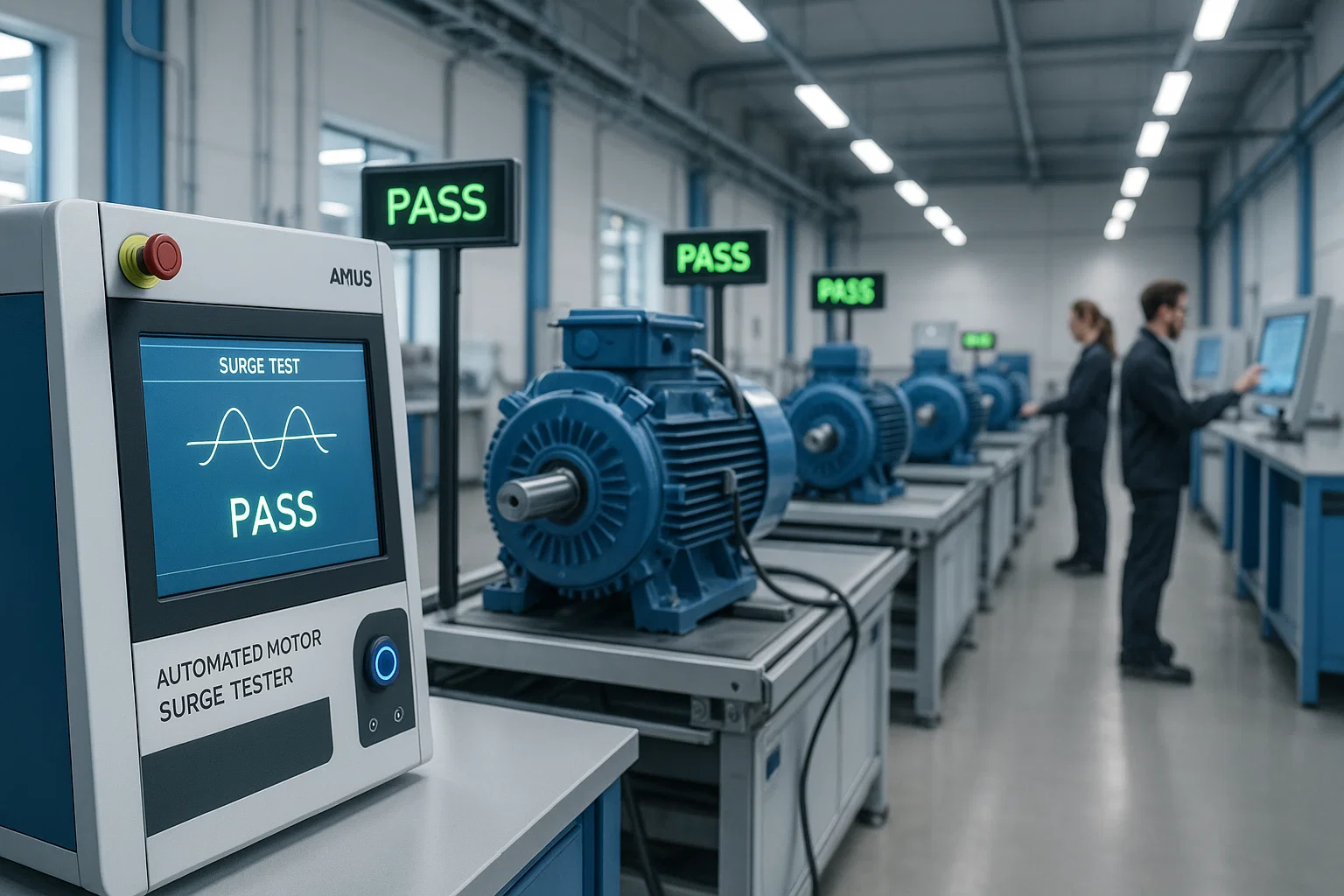
Automated motor testing systems represent advanced diagnostic platforms that evaluate electrical motor performance with minimal human intervention. These sophisticated solutions combine hardware and software components to execute comprehensive testing protocols, including insulation resistance verification, winding continuity assessment, and performance characteristic analysis.
Modern automated testing infrastructure incorporates digital surge testers, hipot testing modules, and data acquisition systems that work cohesively to identify manufacturing defects, installation errors, and potential failure points. Unlike manual approaches requiring technician expertise for each test, automated systems execute standardized procedures consistently while documenting results in centralized databases.
The core components include programmable test sequences, automated data logging, real-time reporting dashboards, and integration capabilities with manufacturing execution systems. This architecture enables manufacturers to transition from reactive quality control to proactive defect prevention strategies.
Manufacturing operations implementing automated motor testing typically realize 40-60% reduction in quality control labor costs within the first year. The elimination of manual test procedures accelerates throughput while freeing skilled technicians for higher-value engineering tasks.
Labor efficiency gains manifest through:
Beyond immediate cost reductions, automated testing systems generate substantial indirect value through improved product quality and operational reliability. Manufacturers report 70-85% fewer field failures when implementing comprehensive automated testing protocols.
Quality improvement translates to:
Equipment failures in production environments cost manufacturing operations between $10,000 and $250,000 per hour depending on industry segment. Predictive maintenance enabled by regular automated testing identifies degradation patterns before catastrophic failures occur.
Facilities implementing automated motor testing report 45-60% reduction in unplanned downtime through early warning detection systems that trigger preventive maintenance activities.

Successful implementation begins with comprehensive facility assessment covering existing testing processes, production volumes, quality control requirements, and integration constraints. This foundation phase establishes baseline metrics for ROI measurement.
Critical assessment activities include:
Engage cross-functional teams including production management, quality assurance, maintenance engineering, and IT infrastructure specialists to ensure comprehensive requirement capture.
Technology selection requires balancing capability requirements against budget constraints while ensuring scalability for future expansion. Evaluate suppliers based on equipment reliability, technical support responsiveness, upgrade pathways, and industry-specific expertise.
Key selection criteria encompass:
Consider digital surge testing equipment that offers comprehensive testing capabilities with flexible configuration options suitable for diverse motor applications.
Physical installation requires coordinated planning to minimize production disruption while ensuring proper integration with existing manufacturing systems. Professional installation teams should execute electrical connections, safety interlocks, and initial calibration procedures.
Installation priorities include:
Leverage experienced installation partners familiar with industrial motor testing applications to accelerate deployment timelines.
Comprehensive validation ensures testing accuracy meets specification requirements while training programs develop operator competency. Execute parallel testing comparing automated results against manual baseline measurements to verify system performance.
Validation activities encompass:
Implement structured training covering operation procedures, maintenance protocols, troubleshooting techniques, and safety requirements. Consider different learning styles through hands-on practice, video tutorials, and reference documentation.
Modern automated testing platforms integrate seamlessly with manufacturing execution systems (MES) enabling real-time production monitoring and quality data correlation. This connectivity creates bidirectional communication where test results automatically update work order status while MES provides context data enhancing traceability.
Integration benefits include:
Consider systems supporting industry-standard communication protocols including OPC-UA, Modbus TCP, and MQTT for flexible integration options.
Advanced automated testing systems capture granular performance data enabling sophisticated analytics that identify degradation trends and predict maintenance requirements. Machine learning algorithms analyze historical test results to establish baseline performance patterns and detect anomalies indicating impending failures.
This predictive capability transforms maintenance strategies from reactive firefighting to planned interventions that minimize disruption and optimize maintenance resource allocation. Understanding motor winding failure signs helps establish appropriate monitoring thresholds.
Comprehensive cost analysis must account for all implementation expenses including equipment acquisition, installation labor, training programs, system integration, and ongoing maintenance requirements.
Typical investment breakdown:
For medium-scale manufacturing operations, total investment typically ranges from $75,000 to $250,000 depending on capability requirements and integration complexity. Understanding the difference between various testing methodologies helps optimize equipment selection.
Most manufacturers achieve positive ROI within 18-36 months through combined labor savings, quality improvements, and downtime reduction. Operations with high production volumes or expensive warranty claims often realize payback within 12-18 months.
Accelerated payback factors include:
Calculate your specific payback period using conservative assumptions accounting for implementation delays and gradual productivity ramp-up during the learning curve period.
Experienced technicians often resist automated systems perceiving them as threats to job security or skill relevance. This resistance manifests through subtle sabotage, reluctant adoption, or active opposition during implementation.
Mitigation strategies:
Legacy manufacturing systems often lack modern communication capabilities creating integration obstacles. Proprietary protocols, incompatible data formats, and network security constraints complicate connectivity.
Resolution approaches:
Automated testing accuracy depends on regular calibration and preventive maintenance that many facilities neglect. Drifting calibration compromises test reliability while equipment failures disrupt production schedules.
Prevention strategies:
Understanding proper maintenance and calibration procedures ensures sustained testing accuracy and equipment longevity.
Select testing platforms offering modular expansion capabilities accommodating production growth and evolving quality requirements. Scalable architectures support additional testing stations, expanded voltage ranges, and enhanced functionality without complete system replacement.
Scalability features include:
Next-generation automated testing incorporates artificial intelligence, advanced analytics, and cloud connectivity delivering enhanced diagnostic capabilities. Position your investment to leverage these emerging technologies through platforms supporting software updates and modular hardware enhancements.
Future capabilities encompass:
Stay informed about innovations in motor testing standards that may influence future testing requirements.
Surge testing represents the most effective method for detecting turn-to-turn insulation failures in motor windings that other testing approaches miss. This technique applies high-voltage impulses while monitoring waveform characteristics revealing insulation weaknesses invisible to resistance measurements.
Modern digital surge testers offer precise waveform analysis, automated comparison algorithms, and comprehensive documentation capabilities essential for quality control programs. Understanding the distinction between surge and hipot testing methodologies helps optimize testing protocols.
Surge testing advantages include:
High-potential (hipot) testing complements surge testing by evaluating insulation integrity between windings and ground. Combined surge and hipot testing provides comprehensive motor quality verification addressing both turn-to-turn and ground insulation failures.
Integrated testing platforms executing both methodologies streamline quality control while reducing equipment investment and floor space requirements. Learn more about hipot functionality in surge testing systems to maximize testing coverage.
Different motor types and applications require tailored testing approaches optimizing detection sensitivity and throughput. Armature testing demands specialized capabilities addressing unique geometric and electrical characteristics distinct from stator testing requirements.
Facilities producing diverse motor types benefit from flexible testing platforms supporting multiple test methodologies. Explore specialized armature testing solutions designed for specific manufacturing requirements.
Even automated systems encounter operational challenges requiring systematic troubleshooting approaches. Understanding common error patterns accelerates resolution while minimizing production impact.
Frequent issues include:
Comprehensive troubleshooting guidance for common surge tester errors helps maintain optimal system performance.
Continuous improvement processes identify opportunities enhancing testing efficiency, accuracy, and reliability. Regular performance reviews comparing actual results against baseline expectations reveal optimization opportunities.
Optimization strategies encompass:
Understanding electrical testing error patterns enables proactive problem prevention.
Motor applications span voltage ranges from low-voltage consumer products to high-voltage industrial equipment requiring testing systems with appropriate capability ranges. Ensure selected equipment accommodates current production requirements while providing margin for future product development.
Voltage considerations include:
Review available voltage range options matching your specific application requirements.
Intuitive user interfaces reduce operator training requirements while minimizing operation errors. Comprehensive reporting capabilities support quality documentation, trend analysis, and continuous improvement initiatives.
Interface evaluation criteria:
Production environments evolve requiring testing equipment adapting to changing requirements. Flexible systems supporting custom test sequences, adjustable parameters, and diverse motor configurations maximize investment longevity.
Explore LCD-based testing systems offering intuitive operation and flexible configuration options.
Electric vehicle production demands rigorous quality standards with zero-defect expectations. Automated testing systems must deliver 100% inspection coverage with comprehensive documentation supporting traceability requirements.
Automotive-specific requirements:
Industrial motor applications emphasize reliability and longevity requiring testing protocols identifying potential long-term failure modes. Predictive testing approaches correlate manufacturing quality metrics with field performance data.
Aerospace applications mandate exhaustive testing documentation and certification processes. Automated systems must generate comprehensive test records complying with industry specifications while supporting audit requirements.
An automated motor testing system is advanced equipment that electronically tests electric motors for defects, insulation failures, and performance issues with minimal human intervention. It uses digital technology to perform surge tests, hipot tests, and other diagnostic procedures automatically.
Manual testing requires technicians to perform each test step individually, taking 15-30 minutes per motor. Automated systems execute complete test sequences in 2-5 minutes with consistent accuracy, eliminating human error and increasing throughput by 300-500%.
Modern automated testing systems achieve 99.5% or higher accuracy rates when properly calibrated. They eliminate human error factors like inconsistent probe placement, incorrect voltage settings, and subjective waveform interpretation.
Automated systems detect most common motor failures including turn-to-turn shorts, ground faults, open circuits, phase imbalances, and insulation degradation. However, some mechanical issues like bearing wear require different diagnostic approaches.
Most manufacturers achieve ROI within 18-36 months through labor savings, quality improvements, and reduced warranty claims. High-volume facilities often see payback in 12-18 months with 200-300% three-year returns.
Automated motor testing systems represent transformational investments delivering measurable returns through enhanced quality, operational efficiency, and predictive maintenance capabilities. Successful implementation requires strategic planning, appropriate technology selection, and comprehensive change management addressing both technical and human factors.
Organizations embracing automated testing position themselves competitively through superior product quality, reduced warranty costs, and accelerated production cycles. The technology evolution continues advancing capabilities while reducing investment thresholds making automation accessible to diverse manufacturing operations.
Begin your automation journey with thorough assessment, realistic expectation setting, and commitment to continuous improvement. The path to automated testing excellence demands patience during implementation but delivers sustained competitive advantages rewarding organizations prioritizing quality and operational excellence.
Ready to explore automated testing solutions for your facility? Contact our technical specialists to discuss your specific requirements and develop customized implementation strategies aligned with your operational objectives and investment parameters.