

Electric vehicle manufacturers face unprecedented quality challenges as global EV production surges toward 15 million units annually. A single motor defect cascading through production lines triggers recalls, warranty claims, and significant brand damage that impacts market position and customer trust. Comprehensive motor testing protocols eliminate these risks by detecting insulation weaknesses, thermal management failures, and performance deviations before vehicles reach customers, ensuring every EV motor delivers the reliability and efficiency that defines electric mobility excellence.
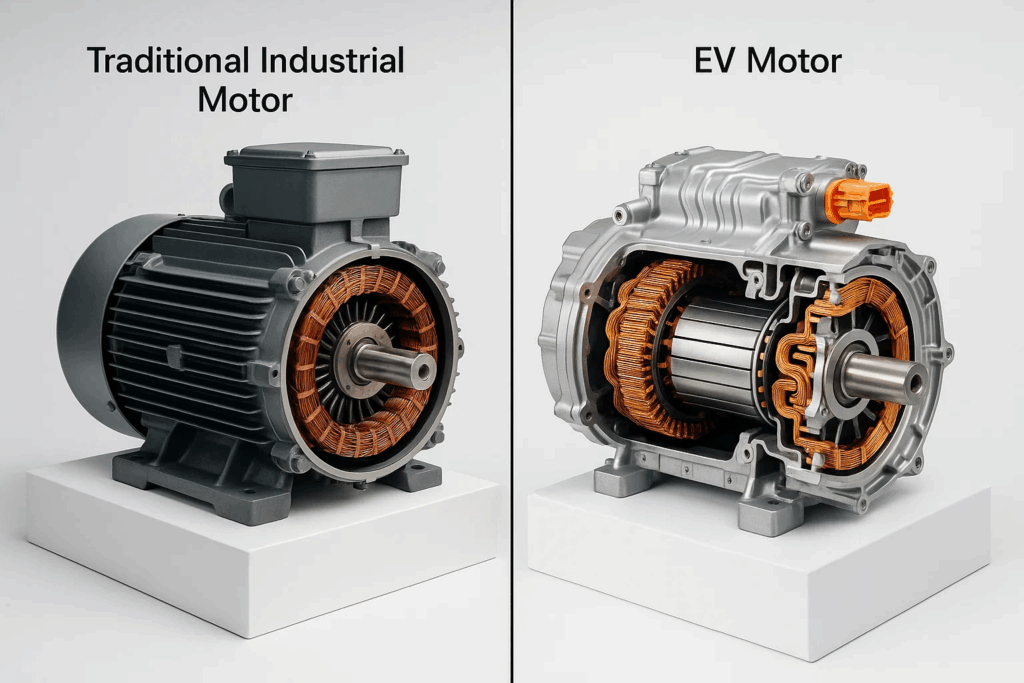
Electric vehicle propulsion motors operate under dramatically different conditions than industrial motors, demanding specialized testing approaches that address unique performance parameters and safety requirements. EV motors endure rapid acceleration cycles, regenerative braking loads, extreme temperature fluctuations, and continuous high-power operation that stress components beyond traditional motor applications.
High-speed operation requirements push many EV motors beyond 15,000 RPM, with performance variants exceeding 20,000 RPM. These speeds generate mechanical stresses and electromagnetic phenomena requiring specialized testing equipment and procedures unavailable in standard motor testing facilities.
Power density demands compress hundreds of kilowatts into compact packages measuring mere inches across. This concentration creates thermal challenges demanding rigorous cooling system validation and temperature monitoring across operational ranges spanning arctic conditions to extreme desert heat.
Voltage levels in EV applications typically range from 400V to 800V systems, with emerging architectures approaching 1000V. These high voltages introduce electrical safety considerations and insulation requirements far exceeding industrial motor standards, necessitating comprehensive high-potential testing protocols.
Inverter integration creates complex motor-controller interactions requiring system-level validation beyond component testing. The power electronics introduce harmonics, switching frequencies, and voltage transients that traditional motor testing overlooks, yet significantly impact motor performance and longevity.
EV motor testing operates within a complex regulatory landscape combining automotive safety standards with electrical equipment requirements. Manufacturers must navigate these intersecting frameworks ensuring compliance across global markets while maintaining production efficiency.
ISO and IEC standards form the foundation of international EV motor testing. ISO 16750 establishes environmental conditions and testing for electrical equipment in road vehicles, while IEC 60034 series defines rotating electrical machine requirements. These standards specify test procedures, performance criteria, and documentation requirements for motor validation.
FMVSS No. 305a, recently updated by NHTSA, establishes comprehensive electric vehicle safety requirements including propulsion battery performance and electrical safety criteria. This standard harmonizes U.S. regulations with Global Technical Regulation No. 20, creating consistent safety expectations across major automotive markets.
Regional compliance requirements add complexity as manufacturers address market-specific regulations. European Union standards emphasize electromagnetic compatibility and environmental impact, while Chinese GB/T standards specify unique testing protocols for electric vehicle components.
LV 123 and LV 124 standards address electrical and electronic components in vehicles, establishing requirements for high-voltage component testing and low-voltage system integration. These automotive industry standards ensure components withstand the demanding environmental conditions vehicles encounter throughout their operational lifespan.
Functional safety standards including ISO 26262 apply to safety-critical motor control systems, requiring rigorous validation of failure modes and safety mechanisms. Compliance demands comprehensive testing documentation and traceability throughout development and production phases.
Understanding differences between motor testing standards helps manufacturers navigate these complex requirements effectively.
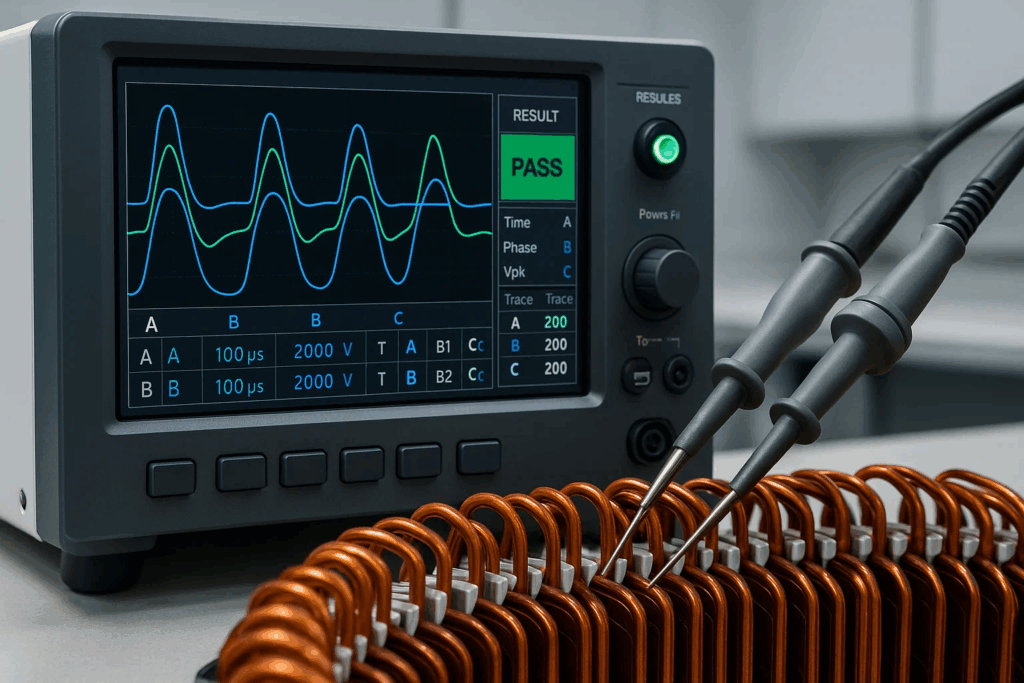
Insulation integrity represents the primary defense against electrical failures threatening vehicle safety and motor reliability. Comprehensive insulation testing begins early in production, continuing through final assembly validation to ensure consistent protection throughout motor operation.
Pre-impregnation testing verifies basic insulation properties before protective coatings are applied, establishing baseline measurements that guide manufacturing process control. Technicians measure resistance between windings and between windings and ground, detecting manufacturing defects before subsequent processes compound issues.
Post-impregnation validation confirms impregnation processes effectively sealed winding insulation, preventing moisture ingress and enhancing dielectric strength. Testing applies voltages appropriate to motor design specifications while monitoring leakage currents indicating incomplete impregnation or contamination.
Megger testing provides rapid insulation assessment using DC voltage application and resistance measurement. While valuable for initial screening, megger testing alone proves insufficient for comprehensive EV motor validation, requiring supplementation with surge and partial discharge testing for complete defect detection.
Surge testing remains the most effective method for detecting turn-to-turn insulation failures invisible to resistance-based testing approaches. This technique applies high-voltage impulses to motor windings while analyzing resultant waveforms, revealing subtle insulation degradation that leads to catastrophic failures under operational stress.
Waveform analysis compares impedance signatures between identical motor phases, identifying minute variations indicating insulation breakdown or winding irregularities. Advanced digital surge testing equipment provides precise waveform capture and automated comparison algorithms, enabling rapid testing without sacrificing detection sensitivity.
Testing voltage selection balances fault detection sensitivity against insulation stress risk. EV motor applications typically employ surge voltages 2-3 times rated operating voltage, sufficient to stress weak insulation points without damaging healthy windings. Understanding surge testing fundamentals optimizes test parameter selection.
Comparative testing methodology establishes reference waveforms from known-good motors, enabling automated pass-fail decisions based on statistical variation analysis. This approach eliminates subjective interpretation while maintaining high detection reliability across production volumes.
Manufacturers should recognize the distinction between surge and hipot testing methodologies to implement comprehensive quality protocols.
Hipot testing evaluates insulation integrity between motor windings and ground by applying sustained high voltage while monitoring leakage current. This destructive testing approach validates motor withstand voltage ratings and verifies manufacturing processes maintain adequate safety margins.
AC hipot testing typically applies voltages at twice the rated motor voltage plus 1000V for one minute duration, detecting insulation weaknesses that could lead to ground faults. The alternating current stresses insulation similarly to operational conditions while providing sensitive leakage detection through current monitoring.
DC hipot alternatives offer faster testing cycles and reduced capacitive charging currents, enabling higher throughput in production environments. However, DC testing provides different insulation stress patterns requiring voltage adjustments maintaining equivalent testing effectiveness to AC approaches.
Learn more about hipot testing integration with comprehensive motor testing systems.
Partial discharge detection identifies early-stage insulation degradation through sensitive monitoring of minute electrical discharges within insulation systems. This advanced diagnostic technique predicts motor reliability by quantifying insulation condition before failures manifest during operation.
Detection sensitivity measures partial discharge activity at picocoulomb levels, revealing insulation defects invisible to conventional testing methods. The technique applies operating voltages while monitoring electromagnetic emissions characteristic of discharge phenomena, providing non-destructive assessment of insulation quality.
Pattern recognition analysis distinguishes between normal operational phenomena and defect-related discharge patterns through sophisticated signal processing. Modern testing systems employ machine learning algorithms trained on extensive discharge datasets, enabling automated defect classification and severity assessment.
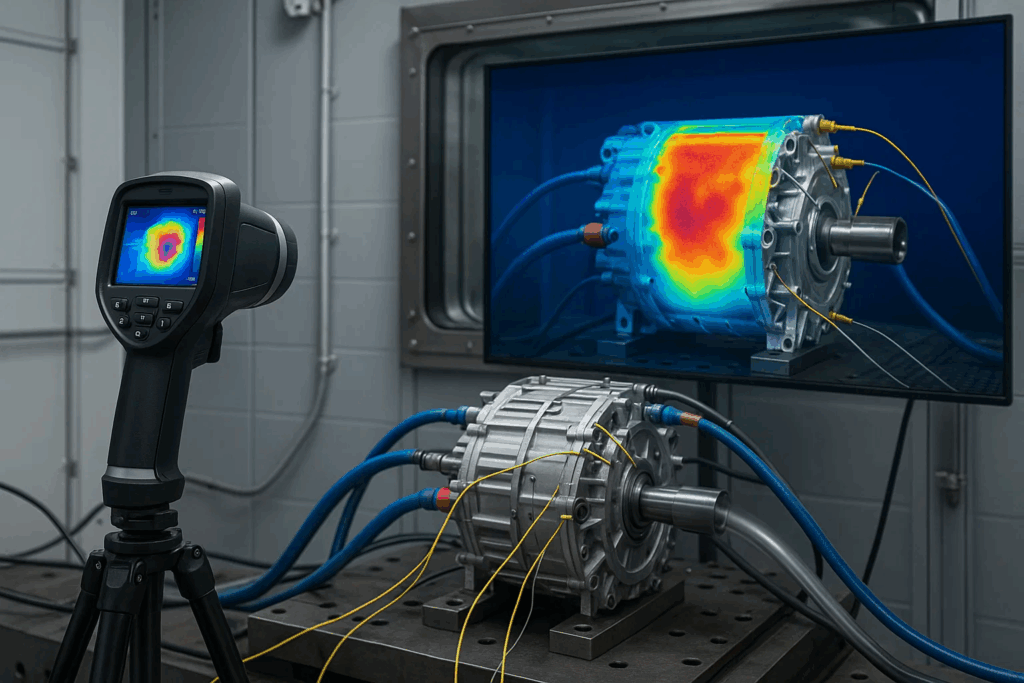
Thermal behavior directly impacts EV motor performance, efficiency, and longevity, making comprehensive thermal testing essential for quality assurance. Testing protocols evaluate motor thermal response across operational ranges, validating cooling system effectiveness and identifying hot spots indicating design or manufacturing issues.
Thermal imaging during loaded testing reveals temperature distribution across motor components, detecting uneven heating patterns suggesting manufacturing defects or inadequate thermal management. Infrared cameras capture comprehensive thermal maps while motors operate under simulated driving cycles, generating data validating thermal models.
Embedded temperature sensors provide continuous monitoring of critical components including windings, bearings, and power electronics. Testing protocols verify sensor accuracy, placement effectiveness, and control system response to thermal events, ensuring protective systems reliably prevent thermal damage.
Heat run testing operates motors under sustained high-power conditions until thermal equilibrium, establishing steady-state temperature profiles validating thermal design assumptions. These extended tests reveal thermal limitations determining continuous power ratings and necessary derating factors for sustained operation.
Motor efficiency directly impacts vehicle range and energy consumption, making accurate efficiency measurement critical for meeting regulatory requirements and customer expectations. Testing employs precision dynamometers measuring mechanical output while power analyzers capture electrical input, calculating efficiency across operational speed and torque ranges.
Dynamometer testing provides controlled load conditions enabling repeatable efficiency measurements across motor operating envelopes. Advanced dynamometers simulate realistic driving cycles including rapid acceleration, regenerative braking, and sustained highway cruising, generating comprehensive performance maps validating motor specifications.
Power analyzer precision becomes crucial as high motor efficiencies demand measurement accuracy better than 0.1% to reliably characterize performance. Modern analyzers employ 18-bit resolution and advanced harmonic analysis capturing power quality parameters affecting efficiency calculations, ensuring results meet international test standard requirements.
Mapping efficiency curves across speed and torque ranges identifies optimal operating zones while revealing efficiency penalties at partial loads and high speeds. This data guides vehicle control strategies maximizing range while validating that motors meet efficiency class requirements under regulatory standards like IEC 60034-30-1.
Acoustic performance significantly influences customer perception of EV quality, elevating NVH testing to critical importance in motor validation programs. Silent electric operation amplifies motor noise ordinarily masked by engine sounds, demanding rigorous acoustic optimization and quality control.
Sound pressure measurements quantify acoustic emissions across motor operating ranges, identifying resonances, electromagnetic noise, and mechanical vibrations requiring mitigation. Testing employs anechoic chambers eliminating environmental noise contamination while precision microphone arrays map sound distribution patterns.
Vibration analysis detects mechanical imbalances, bearing irregularities, and structural resonances degrading motor performance and reliability. Accelerometers monitor vibration spectra during speed sweeps, revealing characteristic frequencies associated with specific fault conditions enabling targeted corrective actions.
Order tracking analysis correlates acoustic and vibration phenomena with motor rotational speed, distinguishing electromagnetic excitation from mechanical sources. This sophisticated analysis technique enables engineers to identify root causes of NVH issues, guiding design improvements and manufacturing process optimization.
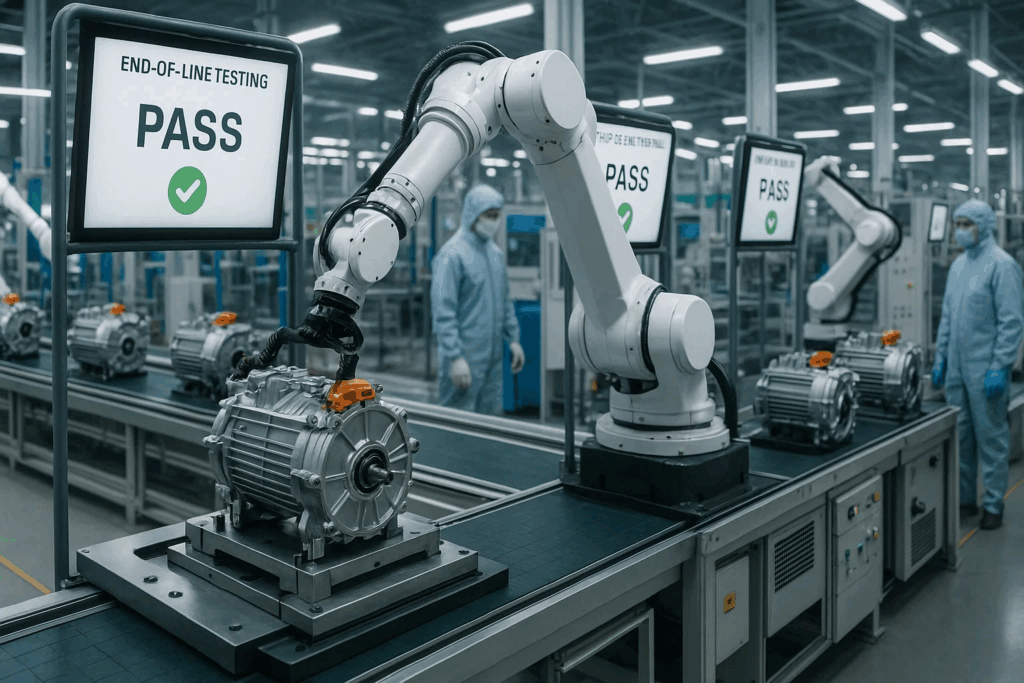
End-of-line testing represents the final quality gate ensuring every motor meets specifications before installation into vehicles. These automated test sequences combine electrical, mechanical, and functional validation in rapid cycles maintaining production throughput while detecting defects missed during process monitoring.
Loaded testing applies torque loads simulating vehicle operation, validating motor performance under realistic conditions. Test stations couple motors to dynamometers or braking systems, executing speed and torque profiles while monitoring electrical parameters, temperatures, and mechanical characteristics against specifications.
Unloaded testing provides rapid functional verification through no-load operation, detecting catastrophic failures and basic functional defects without extensive test duration. These quick checks validate motor rotation, phase configuration, and basic electrical characteristics before proceeding to comprehensive loaded testing.
Automated test execution eliminates operator variability while accelerating throughput, with modern systems completing comprehensive test sequences in 3-5 minutes per motor. Programmable test controllers execute standardized protocols consistently across production shifts, generating detailed documentation supporting quality traceability.
Production testing data enables sophisticated statistical analysis identifying process drift, component variations, and emerging quality trends before defects reach customers. Manufacturing facilities implement real-time monitoring dashboards presenting quality metrics guiding immediate corrective actions.
Control charting tracks key motor parameters including resistance variations, insulation resistance levels, and performance characteristics across production batches. Statistical process control identifies when measurements approach specification limits, triggering interventions preventing defective production.
Correlation analysis reveals relationships between manufacturing process variables and motor quality characteristics, guiding optimization efforts improving yields while reducing warranty exposure. Data mining techniques identify subtle patterns invisible to manual monitoring, enabling proactive quality management.
Understanding motor winding failure patterns helps establish appropriate monitoring parameters and control limits.
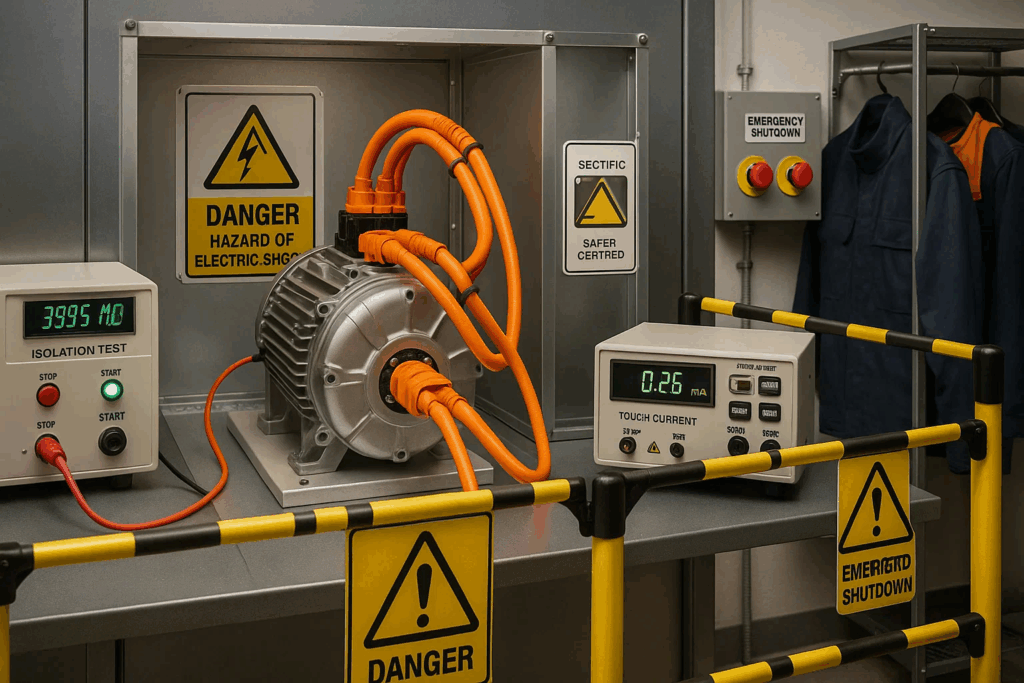
High-voltage electrical systems in EVs introduce safety hazards demanding rigorous validation protocols ensuring vehicle occupant protection and service technician safety. Testing verifies insulation barriers, protective interlocks, and emergency disconnect systems function reliably under normal and fault conditions.
Isolation resistance testing confirms adequate electrical separation between high-voltage circuits and vehicle chassis, preventing shock hazards during operation and maintenance. Testing applies specified voltages while measuring leakage currents, ensuring values remain within safety thresholds defined by automotive electrical standards.
Touch current measurements validate that accessible surfaces maintain safe potential differences, protecting occupants from electrical shock during normal vehicle operation and under single-fault conditions. Testing simulates various fault scenarios while monitoring currents through impedances representing human body resistance.
Protective device validation confirms circuit breakers, fuses, and contactors operate correctly isolating high-voltage systems during fault events. Testing applies overcurrent and short-circuit conditions verifying protective devices interrupt power within specified timeframes preventing thermal damage and electrical hazards.
Motor electromagnetic emissions must comply with stringent automotive EMC standards preventing interference with vehicle electrical systems, wireless communications, and external radio services. Testing validates emissions remain within regulatory limits while motors withstand electromagnetic disturbances without performance degradation.
Conducted emissions testing measures electrical noise propagating through motor power connections, ensuring compliance with limits protecting vehicle electrical systems. Testing employs specialized equipment capturing emissions across frequency ranges defined in automotive EMC standards.
Radiated emissions assessment quantifies electromagnetic fields generated during motor operation, validating compliance with regulations protecting radio services and nearby electronic equipment. Testing occurs in specialized chambers providing controlled electromagnetic environments enabling repeatable measurements.
Immunity testing exposes motors to electromagnetic disturbances simulating real-world interference sources, confirming operation remains stable and safe under challenging conditions. Testing applies conducted and radiated disturbances across frequency ranges while monitoring motor performance and safety system responses.
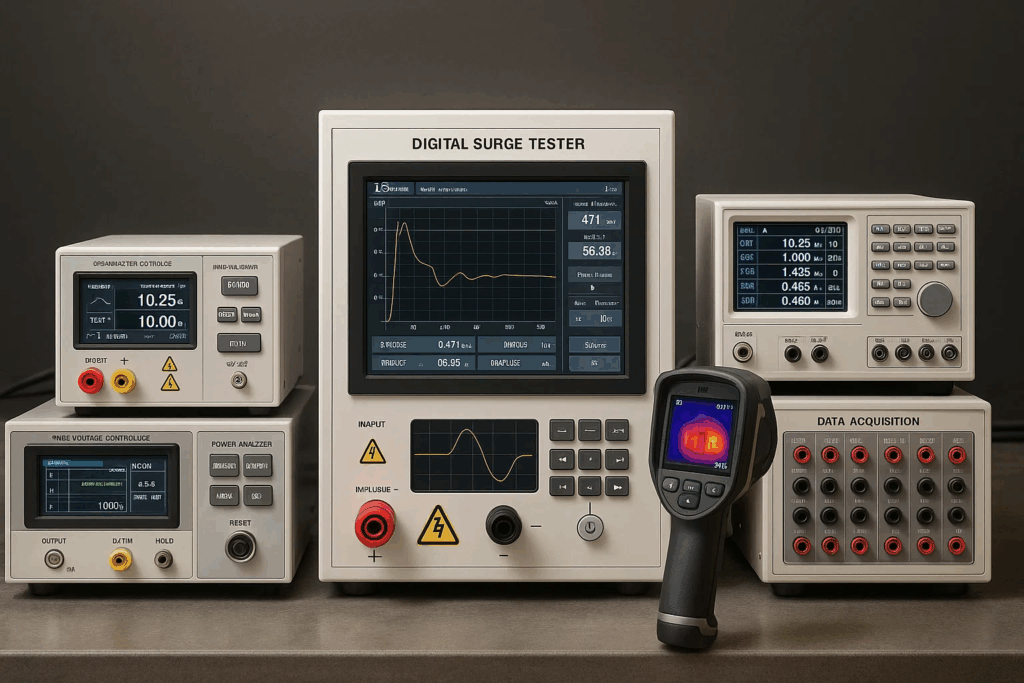
Contemporary motor testing facilities employ integrated systems combining mechanical loading equipment, precision measurement instruments, environmental control, and sophisticated data acquisition infrastructure. This architecture enables comprehensive characterization while maintaining production throughput demands.
Dynamometer integration provides controllable mechanical loading essential for performance validation. Advanced dynamometers accurately simulate vehicle inertia, road load, and regenerative braking conditions while measuring torque and speed with precision sufficient for efficiency calculations meeting regulatory requirements.
High-speed data acquisition captures transient phenomena during rapid acceleration and load changes characteristic of EV operation. Modern systems sample at megahertz rates with synchronized multi-channel capability, enabling detailed analysis of motor behavior during dynamic maneuvers.
Environmental chambers simulate temperature extremes and humidity conditions motors encounter throughout vehicle operational ranges. Thermal chambers maintain stable conditions from arctic cold starts through desert sustained operation, validating thermal management across environmental extremes.
Explore comprehensive testing equipment options supporting EV motor quality assurance programs.
Emerging testing technologies leverage artificial intelligence transforming quality assurance from reactive defect detection to predictive quality management. Machine learning algorithms analyze vast datasets identifying subtle patterns correlating manufacturing variables with motor reliability.
Automated defect classification employs neural networks trained on extensive fault databases, enabling rapid identification of defect types from test signatures. These systems achieve detection accuracy exceeding human experts while maintaining consistency across production volumes and operator shifts.
Predictive maintenance algorithms analyze testing trends forecasting equipment calibration needs and maintenance requirements before measurement drift impacts quality. This proactive approach maintains testing system accuracy while minimizing unplanned downtime disrupting production schedules.
Digital twin technology creates virtual motor models validated against physical testing data, enabling comprehensive simulation exploring operating conditions impractical for physical testing. Engineers employ digital twins optimizing designs and predicting field performance before prototypes exist.
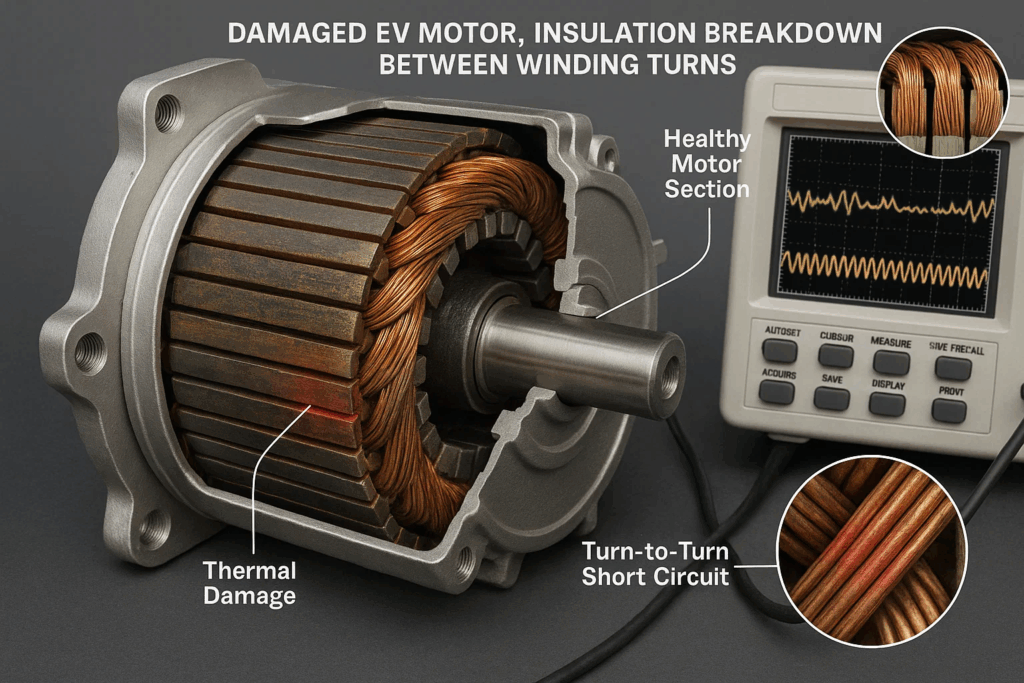
Insulation degradation represents the most frequent EV motor failure mode, resulting from manufacturing defects, thermal stress, contamination, or mechanical damage. Early detection through comprehensive testing prevents catastrophic failures causing vehicle fires, stranding, and expensive warranty claims.
Turn-to-turn shorts develop when insulation between adjacent coil turns breaks down, creating localized current paths generating excessive heat. These faults initially manifest subtly, detectable only through sensitive surge testing comparing impedance signatures between motor phases before thermal damage becomes evident.
Phase-to-phase failures occur when insulation separating motor windings deteriorates, creating unintended electrical paths disrupting motor control. Testing protocols apply specified voltages between phases while monitoring leakage currents, detecting incipient failures before operational stress triggers complete breakdowns.
Ground faults represent serious safety hazards when winding insulation degrades allowing current flow to motor frames. Hipot testing validates ground insulation integrity throughout production, ensuring adequate safety margins protecting vehicle occupants from electrical shock hazards.
Comprehensive understanding of surge testing for insulation failures enables effective quality control strategies.
Manufacturing variations, assembly errors, and material defects create mechanical irregularities affecting motor performance, noise characteristics, and operational reliability. Testing protocols detect these defects through vibration analysis, acoustic measurements, and loaded operation monitoring.
Rotor imbalance generates vibrations increasing with rotational speed, causing bearing wear, noise, and potential mechanical failure. Dynamic balancing equipment identifies imbalance magnitude and angular location, enabling corrective weight addition or removal before motor assembly completion.
Bearing defects including contamination, improper installation, and manufacturing flaws create characteristic vibration signatures detectable through spectral analysis. Early detection prevents bearing failures causing catastrophic motor damage and potential vehicle safety hazards.
Mechanical interference between rotating and stationary components generates noise and accelerates wear. No-load testing at maximum speed reveals mechanical issues before motors enter service, preventing field failures requiring expensive warranty repairs.
Inadequate cooling system performance limits motor power delivery while reducing operational lifespan through accelerated insulation aging. Testing validates cooling system effectiveness across environmental conditions, ensuring thermal management maintains components within safe temperature ranges.
Coolant flow restrictions from manufacturing debris, assembly errors, or design inadequacies reduce cooling capacity. Thermal testing under sustained high-power conditions reveals inadequate cooling through excessive temperature rise rates or steady-state temperatures exceeding specifications.
Temperature sensor failures prevent effective thermal protection, risking motor damage from thermal overload conditions. Validation testing confirms sensor accuracy, placement effectiveness, and control system integration ensuring reliable thermal monitoring throughout motor operation.
Understanding proper troubleshooting approaches for testing errors maintains testing system effectiveness.
Successful EV motor testing programs implement layered validation approaches balancing comprehensive defect detection against production throughput requirements. Strategic placement of test stations throughout manufacturing processes enables early defect detection minimizing scrap costs while maintaining final quality gates ensuring customer satisfaction.
In-process testing at critical manufacturing steps detects defects before subsequent operations add value to flawed components. Stator winding verification immediately after coil insertion identifies winding errors before impregnation processes make corrections impractical, dramatically reducing scrap costs.
Subassembly validation confirms component quality before final motor assembly, preventing defective parts from contaminating otherwise acceptable assemblies. Rotor testing validates magnetic properties and mechanical characteristics before integration, while stator testing confirms electrical parameters meet specifications.
Final assembly testing executes comprehensive validation combining electrical, mechanical, and performance testing under loaded conditions simulating vehicle operation. This final quality gate ensures only motors meeting all specifications proceed to vehicle installation, protecting brand reputation while minimizing warranty exposure.
Comprehensive testing generates massive data volumes requiring sophisticated management systems maintaining traceability while enabling analytical insights driving continuous improvement. Modern manufacturing facilities implement integrated data platforms connecting testing equipment, manufacturing execution systems, and quality management databases.
Serialization and tracking associates every test result with specific motor serial numbers, enabling complete traceability from raw materials through vehicle integration. This capability proves essential for efficient recall management and warranty analysis identifying systemic quality issues.
Real-time quality monitoring dashboards present production quality metrics enabling immediate response to emerging issues. Manufacturing teams monitor reject rates, parameter trends, and statistical process control violations, triggering corrective actions before significant quantities of defective motors enter production.
Long-term data retention supports warranty analysis, reliability studies, and continuous improvement initiatives. Archived testing data enables engineers to correlate manufacturing variables with field performance, guiding design improvements and process optimization reducing warranty costs while enhancing customer satisfaction.
Learn about implementing comprehensive surge testing programs across production environments.
Testing system sophistication demands properly trained operators understanding equipment capabilities, test protocols, and troubleshooting procedures. Comprehensive training programs develop operator competency ensuring consistent test execution and appropriate responses to equipment issues or unexpected test results.
Structured training curricula cover equipment operation, safety protocols, quality specifications, and basic troubleshooting procedures. Hands-on practice under supervision develops operator confidence while ensuring understanding of critical testing parameters and their significance to motor quality.
Competency assessment validates operator understanding through written examinations and practical demonstrations before authorizing independent operation. Regular refresher training maintains skills while introducing operators to equipment updates and procedure improvements.
Cross-training initiatives develop operational flexibility enabling facilities to maintain production flow during personnel absences while broadening employee capabilities supporting career development. Multiple operators qualified on each testing station prevent operational bottlenecks during shift transitions or unexpected absences.
Rapid evolution in EV motor design drives corresponding advances in testing capabilities addressing new technologies, higher performance demands, and evolving quality expectations. Testing equipment manufacturers develop next-generation systems incorporating artificial intelligence, advanced sensors, and cloud connectivity.
Non-invasive sensing technologies enable motor condition monitoring during operation without physical connections, streamlining testing while eliminating contact-related measurement uncertainties. Infrared thermal imaging, magnetic field sensing, and acoustic analysis provide comprehensive characterization without test leads or mechanical coupling.
Cloud-based analytics platforms aggregate testing data across manufacturing facilities enabling global quality oversight and benchmarking. Centralized data repositories support advanced analytics identifying quality trends invisible within individual facility data while enabling rapid dissemination of corrective actions across production networks.
Augmented reality integration assists operators through visual guidance overlaying test procedures and troubleshooting information onto equipment views. AR systems reduce training time while improving test execution consistency, particularly beneficial for complex procedures or infrequent operations.
Testing standards continue evolving addressing emerging technologies including silicon carbide inverters, hairpin windings, and ultra-high-speed motors. Standards organizations collaborate with industry developing protocols ensuring testing keeps pace with motor technology advancement.
Hairpin winding testing requires specialized approaches addressing unique geometric configurations and manufacturing processes. Standards development focuses on surge testing adaptations, partial discharge detection techniques, and end-winding insulation validation appropriate for these high-performance winding designs.
Wide bandgap semiconductor considerations influence testing protocols as silicon carbide and gallium nitride inverters introduce higher switching frequencies and voltage transients. Testing standards evolve incorporating appropriate stress testing and insulation validation for motors operating with next-generation power electronics.
Thermal runaway prevention gains emphasis as battery integration with motors creates new safety considerations. Testing protocols expand validating motor operation during thermal events while ensuring electromagnetic compatibility with battery management systems.
EV motors operate at higher speeds (15,000+ RPM), higher voltages (400V-800V), and experience extreme thermal cycles. They require specialized testing for hairpin windings, advanced thermal management validation, high-speed performance characterization, and automotive-specific safety compliance that traditional industrial motor testing doesn’t address.
Key standards include ISO 16750 (automotive electrical equipment), IEC 60034 series (rotating electrical machines), FMVSS No. 305a (EV safety), LV 123/124 (high-voltage components), and ISO 26262 (functional safety). Regional standards like GB/T 18488 in China may also apply depending on target markets.
Surge testing detects turn-to-turn insulation faults within windings that other methods miss, while hipot testing validates insulation between windings and ground for electrical safety. Both are essential: surge testing catches manufacturing defects, hipot testing ensures shock protection compliance.
Critical tests include surge testing for winding faults, hipot for ground insulation, resistance measurements for uniformity, loaded dynamometer performance validation, thermal response testing, NVH assessment, and isolation resistance verification. Automated systems complete these tests in minutes with full traceability.
Thermal testing uses infrared imaging, embedded sensors, and sustained load tests to validate cooling effectiveness across all operating conditions. It confirms motors maintain safe temperatures, preventing insulation degradation, power loss, and failures that impact vehicle range and performance.
Electric vehicle motor quality assurance demands comprehensive testing protocols combining traditional electrical validation with advanced thermal analysis, performance characterization, and safety verification. Manufacturers implementing rigorous testing programs deliver reliable motors meeting stringent automotive requirements while minimizing warranty exposure and protecting brand reputation.
Success requires strategic equipment investment, operator training, data management infrastructure, and continuous improvement commitment. Organizations embracing comprehensive testing as quality cornerstones rather than necessary expenses gain competitive advantages through superior product reliability and customer satisfaction.
The EV industry’s explosive growth intensifies quality demands while accelerating technology evolution. Testing programs must adapt incorporating new technologies, emerging standards, and advanced analytical capabilities maintaining quality excellence throughout this transformative period in automotive history.
Ready to implement world-class EV motor testing in your facility? Contact our technical experts to discuss customized testing solutions aligned with your production requirements and quality objectives.