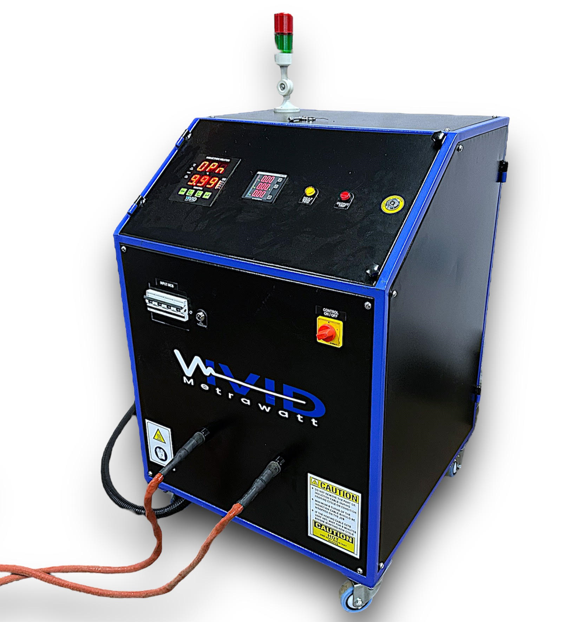
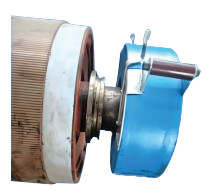
The three-phase voltage is rectified and smoothed. This rectified voltage is then converted by means of an inverter into an AC voltage with a frequency between 10 and 25 kHz. The power is then applied to the workpiece magnetically via a ‘resonance capacitor’ using an inductor (coil). Since the frequency is relatively high, the penetration depth of the magnetic field is not too large, so that only the outer layer of the workpiece is heated. This principle makes heating using medium-frequency particularly suitable for dismantling purposes, such as removing bearing rings from shafts.
This heater consists of a generator and one or more inductors. The generator is designed for the connection of inductors used for heating ferromagnetic workpieces. Suitable materials include iron, steel, stainless steel, titanium and certain bronze alloys. The maximum capacity workpieces can be subjected to is 22 Kw, 33KW or 44 kW, depending on the type of heater
Automotive: Ideal for heat treatment, forging, and component manufacturing.
Aerospace: Precision heating for critical components and assembly processes.
Metal Fabrication: Efficient and consistent heating for welding, bending, and cutting.
Manufacturing and Assembly Lines: Streamlined operations with energy-efficient heating solutions.