

Purchasing an induction heater without adequate safety features puts your workforce at risk, exposes your facility to costly downtime, and could result in catastrophic equipment failure. One faulty component or missing protection system can lead to workplace injuries, fire hazards, or equipment damage costing thousands in repairs and liability. The solution lies in understanding which safety mechanisms are non-negotiable and how they protect both your personnel and your investment in heating technology.
Induction heating systems generate intense electromagnetic fields and extreme temperatures, often exceeding 1000°C in seconds. Without proper safeguards, these powerful machines pose significant risks including electrical shock, thermal burns, electromagnetic interference, and fire hazards.
Industrial facilities report that equipment-related accidents cost an average of $42,000 per incident when factoring in medical expenses, downtime, and regulatory fines. More importantly, worker safety should never be compromised for operational efficiency.
Key safety concerns include:
Understanding how electromagnetic induction works helps operators recognize potential hazards and appreciate the importance of comprehensive safety systems.
Thermal management represents the first line of defense in induction heating safety. These systems prevent dangerous temperature escalations that could damage equipment or cause injuries.
The most critical safety feature is an automatic thermal shutoff that monitors system temperature in real-time. When internal components exceed safe operating thresholds, the system immediately cuts power to prevent damage or fire.
What to look for:
Effective induction heaters incorporate forced-air or liquid cooling systems. Safety-conscious designs include monitoring for:
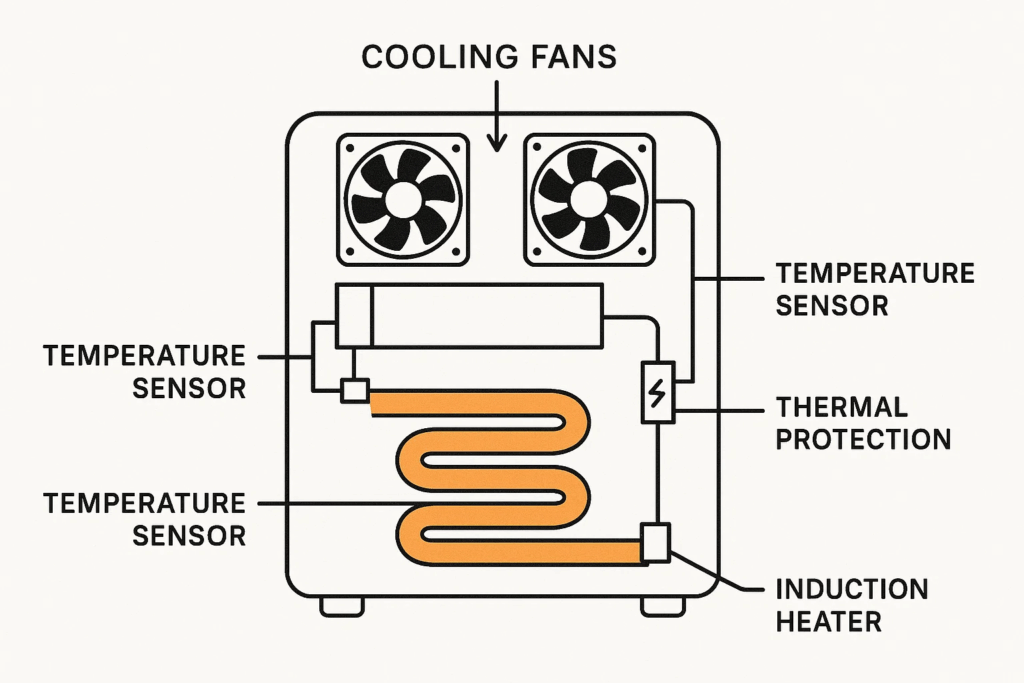
The heating coil itself reaches extremely high temperatures. Premium systems feature:
Induction heaters operate on high-voltage, high-frequency power that demands robust electrical protection to prevent shock hazards and system failures.
Ground fault circuit interrupters (GFCI) detect current leakage and immediately disconnect power when abnormal current paths are detected. This feature is mandatory for wet environments or portable applications.
Advanced induction heating systems include:
Look for systems featuring:
Every induction heater must include clearly marked emergency stop buttons that:

Beyond equipment protection, modern induction heaters incorporate features specifically designed to safeguard operators during daily use.
Quality systems include:
Induction heaters generate strong electromagnetic fields that can interfere with pacemakers and other medical devices. Essential EMF safety features include:
Advanced systems account for PPE requirements by providing:
Leading induction heating manufacturers incorporate sophisticated safety technologies that provide additional protection layers.
Modern systems feature microprocessor-controlled power delivery that:
Connected induction heaters enable:
When selecting the best induction heater for industrial applications, prioritize models offering these advanced monitoring capabilities.
Premium induction heating equipment follows fail-safe design principles where:
Reputable induction heating equipment carries certifications from recognized testing organizations, demonstrating compliance with international safety standards.
UL Listing (Underwriters Laboratories)
CE Marking (European Conformity)
CSA Certification (Canadian Standards Association)
IEC 60519 Compliance
Depending on your application, additional certifications may be necessary:
Different industries have unique safety considerations when implementing induction heating technology.
Induction heaters for the automotive industry require:
When using induction heaters for bearing installation, critical safety features include:
The working principle of bearing induction heaters incorporates specific safety considerations for handling rotating equipment components.
For shrink-fitting and maintenance applications:

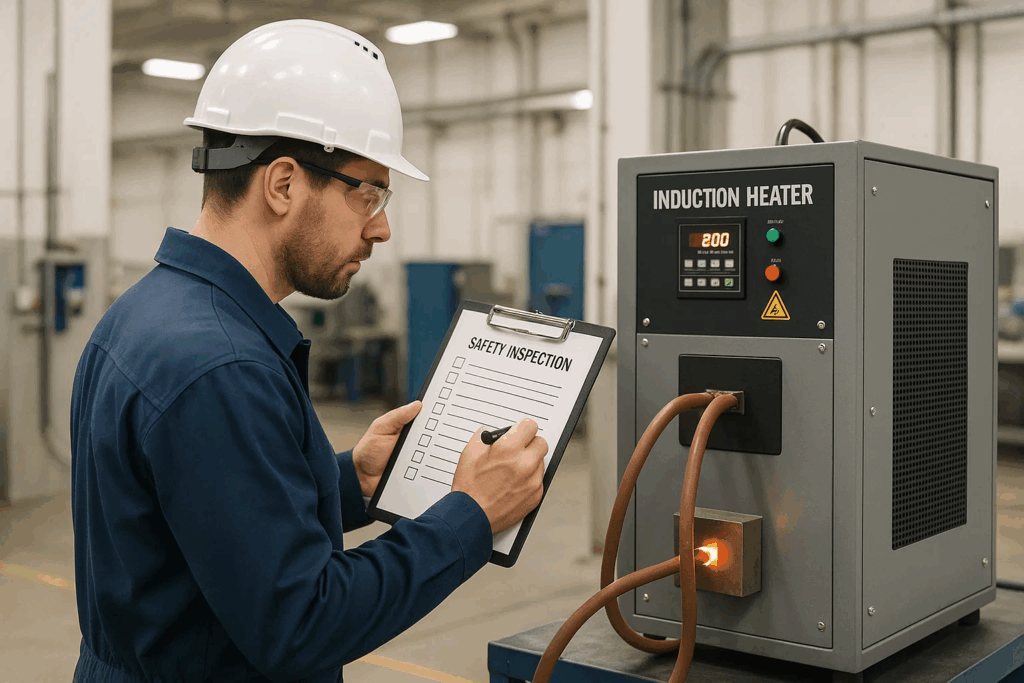
Safety features remain effective only when properly maintained and tested according to manufacturer specifications.
Establish a comprehensive safety inspection schedule including:
Daily Checks:
Monthly Reviews:
Annual Certification:
Maintain detailed records including:
Comprehensive safety training should cover:
The automatic thermal shutdown system is the most critical safety feature. This mechanism continuously monitors temperature levels and immediately cuts power when overheating is detected, preventing equipment damage, fire hazards, and operator injuries. However, comprehensive safety requires multiple protection layers including electrical safeguards, emergency stops, and proper EMF shielding working together.
Verify that your induction heater carries recognized safety certifications such as UL, CE, or CSA markings on the equipment nameplate. Additionally, ensure all safety features are functioning properly through regular testing, check that emergency stop buttons respond immediately, confirm cooling systems operate correctly, and maintain up-to-date maintenance records. Never use equipment with damaged cables, missing guards, or malfunctioning safety indicators.
Yes, the strong electromagnetic fields generated by induction heaters can interfere with pacemakers, implanted defibrillators, and other electronic medical devices. Individuals with such devices should maintain safe distances (typically 3-6 feet minimum) from operating induction heating equipment or avoid these work areas entirely. Employers must post clear warning signs and conduct EMF assessments to identify safe zones. Always consult with medical professionals and equipment manufacturers for specific guidance.
Safety testing should follow a tiered schedule: perform daily checks of emergency stops, cooling systems, and visual inspections; conduct monthly testing of thermal protection systems, electrical insulation, and safety interlocks; and complete annual comprehensive safety audits by qualified technicians including calibration, certification, and full electrical testing. Document all testing in maintenance logs for compliance purposes.
Yes, portable induction heaters require additional safety considerations including stable bases to prevent tipping, secure cable management systems to avoid trip hazards, battery backup for emergency shutdown in field locations, weather-resistant enclosures for outdoor use, and enhanced operator training for varied work environments. Stationary systems benefit from permanent safety installations like fixed guards, integrated ventilation, and hardwired emergency stops, but both types must meet the same fundamental safety standards.
Selecting an induction heater with comprehensive safety features protects your most valuable assets—your employees—while safeguarding your equipment investment and maintaining operational continuity. Non-negotiable safety features include automatic thermal protection, electrical safety mechanisms, emergency stop functionality, proper EMF shielding, and relevant safety certifications.
Key Takeaways:
✓ Prioritize thermal protection systems with automatic shutdown and multiple temperature monitoring points
✓ Verify electrical safety features including ground fault protection, circuit isolation, and emergency stops
✓ Confirm safety certifications from recognized organizations (UL, CE, CSA) appropriate for your region
✓ Choose industry-appropriate features matching your specific application requirements
✓ Implement maintenance protocols ensuring safety systems remain functional throughout equipment life
✓ Invest in comprehensive training empowering operators to work safely and recognize potential hazards
When evaluating induction heating equipment, remember that safety features are investments, not expenses. The cost of implementing proper safeguards pales in comparison to the human and financial costs of workplace accidents. Choose manufacturers who demonstrate commitment to safety through robust design, proper certifications, and comprehensive documentation.
Your decision to prioritize safety features today creates a secure working environment that protects lives, reduces liability, and ensures reliable operation for years to come. Never compromise on safety—your team depends on it.