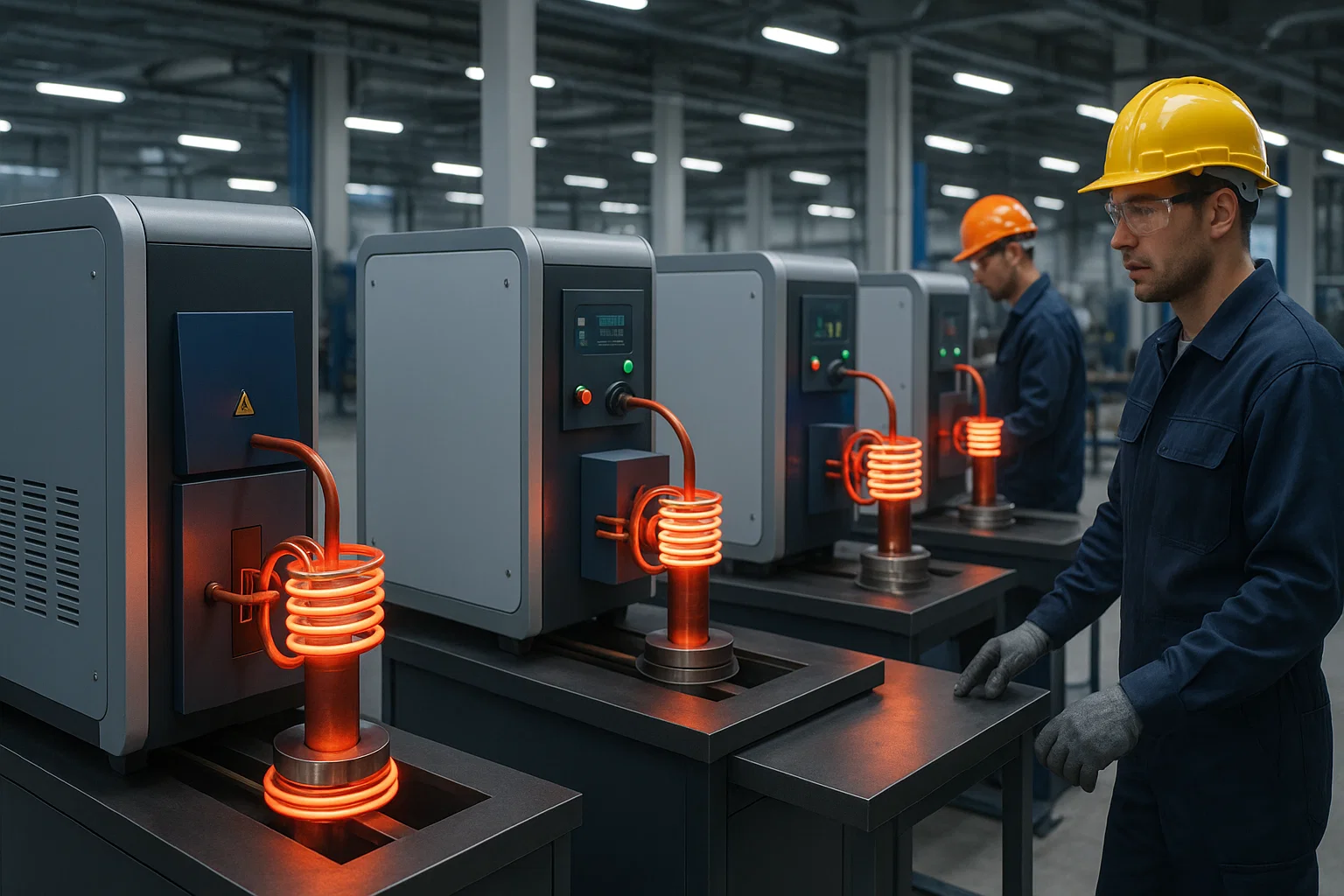


Industrial manufacturers face mounting pressure to increase production efficiency while reducing energy costs and maintaining safety standards. Traditional heating methods often fall short, resulting in inconsistent heating, excessive energy consumption, and safety hazards that can cost companies thousands in downtime and repairs.
Using inadequate heating equipment leads to poor product quality, extended cycle times, increased operational costs, and potential workplace accidents. Many businesses struggle with outdated heating technologies that can’t deliver the precision and efficiency modern manufacturing demands.
The best induction heater for industrial applications transforms manufacturing processes by delivering rapid, precise, and energy-efficient heating that can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% while improving production speeds and product quality.
Industrial induction heating represents a revolutionary approach to heating electrically conductive materials through electromagnetic induction. Unlike traditional heating methods that rely on external heat sources, the heat is generated inside the object itself, instead of by an external heat source via heat conduction. Thus objects can be heated very rapidly.
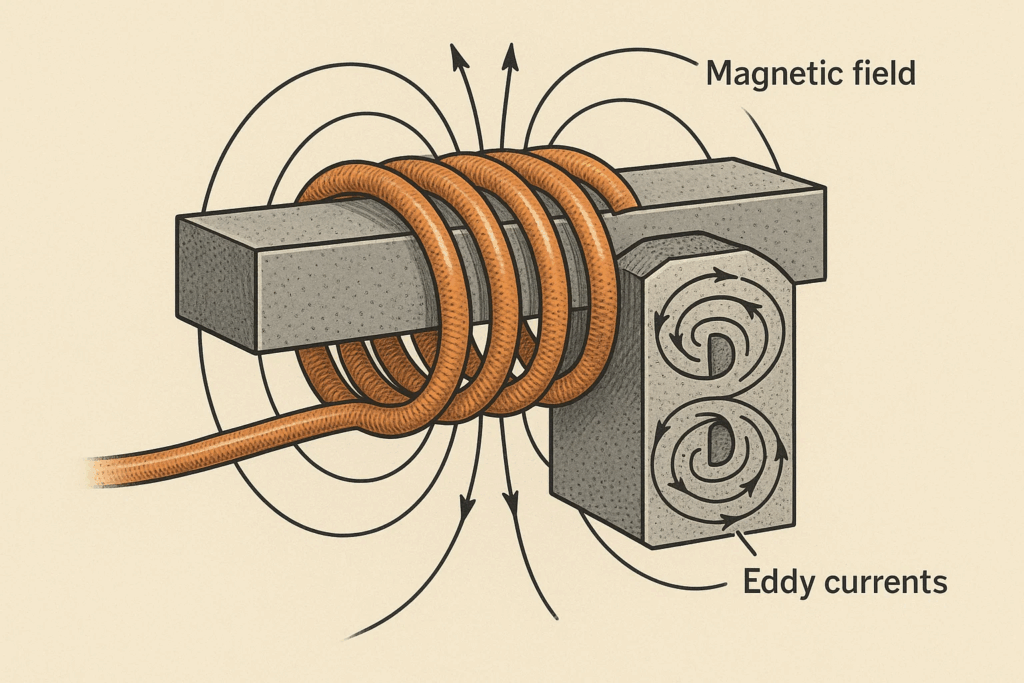
The technology operates by generating an alternating magnetic field through an induction coil, which induces eddy currents within the workpiece material. These currents encounter electrical resistance, creating thermal energy directly within the material structure. This fundamental principle enables unprecedented control over heating patterns, temperatures, and timing.
The process begins when alternating current flows through a water-cooled copper coil, creating a powerful electromagnetic field. When conductive materials enter this field, circulating currents form within the material, generating heat through electrical resistance. The frequency of the alternating current determines penetration depth, while power levels control heating intensity.
For magnetic materials like steel, an additional heating mechanism called hysteresis loss occurs when the alternating magnetic field repeatedly magnetizes and demagnetizes the material’s molecular structure, creating friction and additional heat generation.

Selecting the best induction heater for industrial applications requires careful evaluation of multiple technical and operational factors. The output power of your induction heating power supply determines the relative speed at which your part is heated, making power requirements the primary consideration.
Power specifications typically range from 1 kW for small precision applications to over 1 MW for large-scale industrial operations. The required power depends on:
Operating frequency directly impacts heating effectiveness and penetration depth:
Different materials respond uniquely to induction heating:
Ferromagnetic Materials (Steel, Iron):
Non-Ferromagnetic Metals (Aluminum, Copper, Brass):
Non-Conductive Materials:
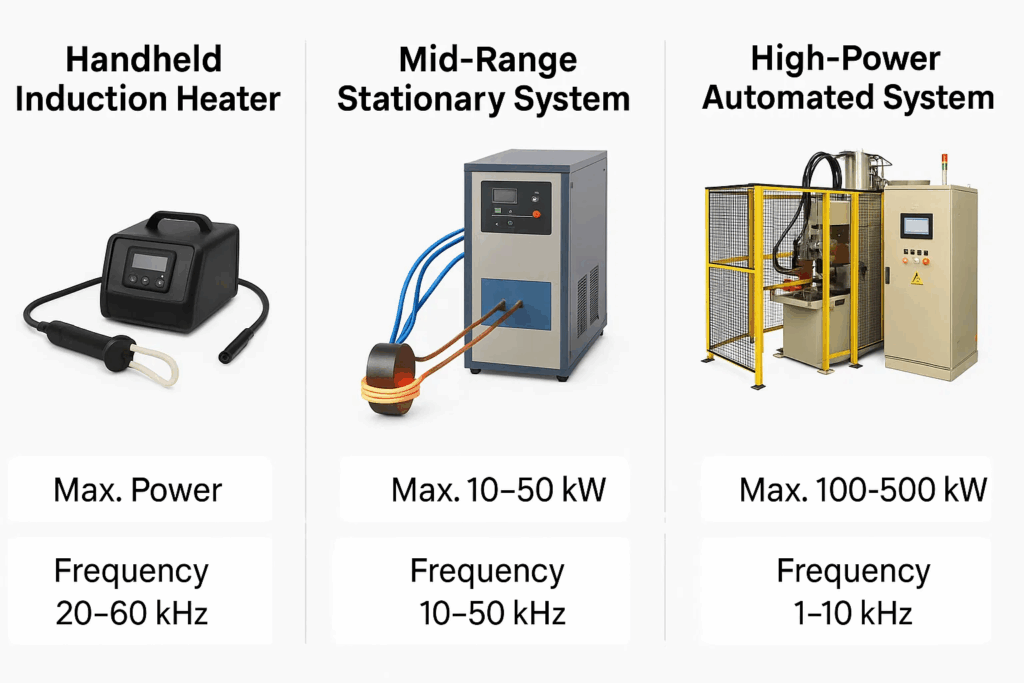
Power Range: 1-3 kW
Best For: Maintenance, repairs, small component heating
Handheld units excel in maintenance applications where portability and precision matter most. These systems typically operate at frequencies between 15-40 kHz and prove invaluable for:
Power Range: 5-50 kW
Best For: Production heating, batch processing
Stationary systems offer the perfect balance between power and precision for most industrial applications. Key advantages include:
Power Range: 50 kW-1+ MW
Best For: High-volume production, continuous processing
Large-scale systems deliver maximum throughput for demanding industrial environments:
Custom Power Ranges
Best For: Unique industrial requirements
Specialized systems address specific industry needs:
Understanding power specifications ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness. Output power, the primary specification, is usually measured in watts (W). Other important ratings include the output current supplied to the heating coil and the output frequency, which is often expressed in kilohertz (kHz).
Accurate power determination requires comprehensive analysis of heating requirements:
Basic Power Formula: P = (Mass × Specific Heat × Temperature Rise) / (Time × Efficiency)
Additional Factors:
Modern induction heaters achieve remarkable efficiency levels:
Power supply specifications impact installation and operation:
Single-Phase Systems:
Three-Phase Systems:
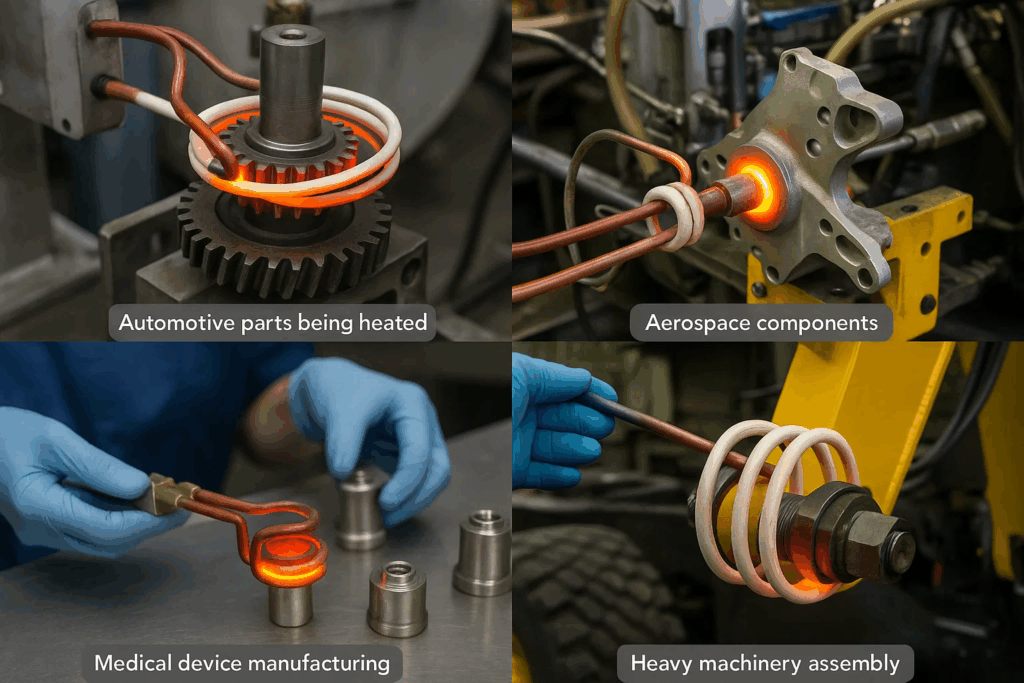
Industries such as metalworking, electronics, and semiconductors heavily rely on induction heating for processes like brazing, hardening, annealing, and soldering. The versatility of induction heating technology enables applications across virtually every manufacturing sector.
The automotive sector represents one of the largest markets for industrial induction heating:
Surface Hardening:
Assembly Operations:
Repair and Maintenance:
For detailed automotive applications, explore our guide on induction heater for the automotive industry.
Precision requirements in aerospace applications demand the highest levels of control:
Large-scale industrial operations benefit from induction heating’s scalability:
Steel and Metal Processing:
Mining and Construction:
Learn more about how electromagnetic induction works in these demanding applications.
High-tech manufacturing requires ultra-precise heating control:
Modern industrial induction heaters incorporate sophisticated technologies that enhance performance, safety, and operational efficiency. These advanced features distinguish premium systems from basic heating equipment.
Contemporary induction heaters feature intelligent control systems that provide:
Microprocessor-Based Operation:
User Interface Enhancements:
Industrial safety requirements demand comprehensive protection systems:
Automatic Safety Controls:
Environmental Monitoring:
Industry 4.0 compatibility enables advanced manufacturing integration:

Proper maintenance ensures reliable operation and extends equipment life while maintaining safety standards. Understanding troubleshooting electrical testing errors helps prevent costly downtime.
Daily Inspections:
Weekly Maintenance Tasks:
Monthly Comprehensive Service:
Industrial induction heating requires adherence to strict safety procedures:
Personnel Safety Requirements:
Equipment Safety Standards:
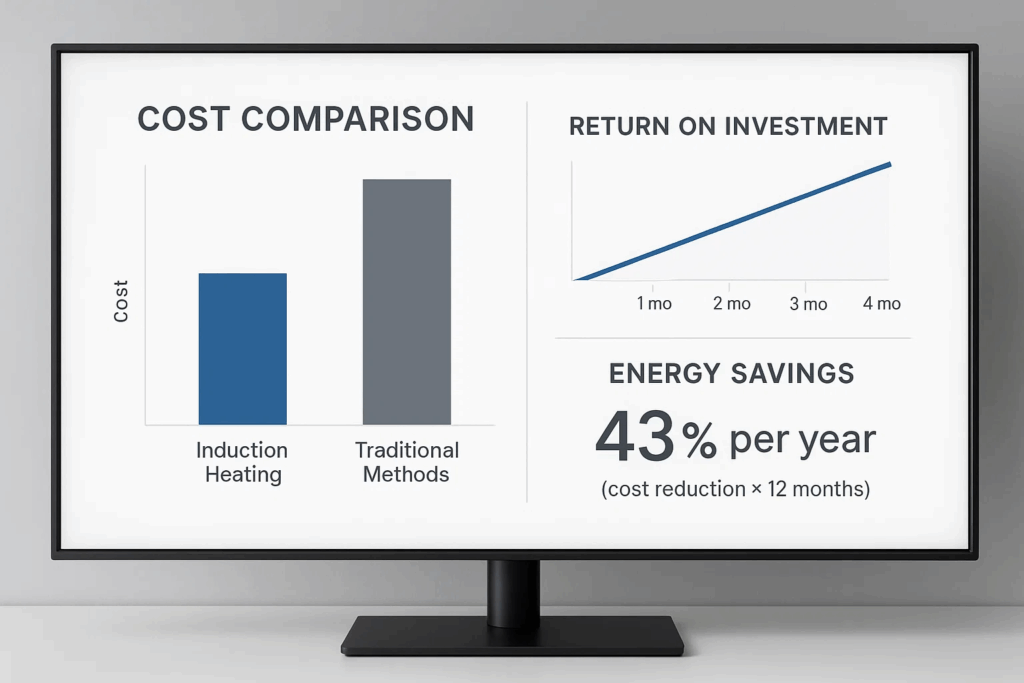
Understanding the financial impact of industrial induction heater selection requires comprehensive analysis of initial investment, operational costs, and long-term benefits. Inductive heating uses up to 40% less energy than conventional methods, creating significant cost savings opportunities.
Equipment Costs by Category:
Installation and Setup Costs:
Energy Consumption Benefits:
Labor Cost Savings:
Typical ROI periods for industrial induction heating systems:
Small Systems (Under 25 kW): 1-2 years Medium Systems (25-100 kW): 2-3 years
Large Systems (Over 100 kW): 2-4 years
ROI Acceleration Factors:
The industrial induction heating industry continues evolving with technological advancement and changing manufacturing requirements. Understanding future trends helps guide long-term equipment investment decisions.
Semiconductor Technology Improvements: Advanced silicon carbide (SiC) and gallium nitride (GaN) semiconductors enable higher efficiency and more compact designs. Learn about high-efficiency induction heating with SiC GaN semiconductors.
Digital Twin Technology: Virtual modeling capabilities allow optimization of heating processes before physical implementation, reducing development time and improving performance predictability.
Artificial Intelligence Integration: Machine learning algorithms optimize heating parameters in real-time, adapting to material variations and environmental conditions for consistent results.
Energy Efficiency Improvements: Next-generation systems target 95%+ energy conversion efficiency while maintaining precise temperature control and rapid heating capabilities.
Renewable Energy Integration: Compatibility with solar and wind power sources becomes increasingly important as manufacturers pursue carbon neutrality goals.
Waste Heat Recovery: Advanced systems capture and utilize waste heat for facility heating or other processes, further improving overall energy efficiency.
Connected Manufacturing: Seamless integration with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and enterprise resource planning (ERP) platforms enables optimized production scheduling and resource allocation.
Predictive Analytics: Advanced sensors and data analysis predict maintenance needs, quality issues, and process optimization opportunities before problems occur.
Remote Operation: Cloud-based control systems enable expert technicians to monitor and adjust systems from anywhere, reducing travel costs and improving response times.
Selecting the best induction heater for industrial applications requires balancing technical requirements, operational needs, and financial constraints. The most effective approach involves systematic evaluation of your specific heating requirements, careful consideration of available technologies, and consultation with experienced suppliers.
Key Decision Factors:
Success Indicators:
The best induction heater for industrial applications combines precision, efficiency, and reliability to transform manufacturing processes. Modern induction heating technology delivers unmatched performance through electromagnetic heating principles that generate heat directly within workpieces, enabling rapid, controllable, and energy-efficient processing.
Industrial induction heaters represent a strategic investment that pays dividends through reduced energy costs, improved production efficiency, enhanced safety, and superior product quality. The technology’s continued evolution ensures long-term value and competitive advantage for forward-thinking manufacturers.
Success with industrial induction heating depends on matching system capabilities to specific application requirements while considering future growth and technological advancement. By following the selection criteria and considerations outlined in this guide, manufacturers can confidently choose systems that deliver optimal performance and return on investment.
For specialized applications and expert guidance, explore our comprehensive resources on smart induction heating precision efficiency industry and induction heating renewable energy applications.
About VividmetraWatt Global: Leading provider of advanced induction heating solutions for industrial applications worldwide. Our expertise spans system design, installation, training, and ongoing support to ensure optimal performance and return on investment.
Ready to Transform Your Industrial Heating Process? Contact our technical specialists for personalized consultation and system recommendations tailored to your specific requirements.